We spend more time confirming our identity than you realize. Inputting a password, giving a signature of approval, and presenting photo identification to vote in an election, are a few examples of the lengths we go to prove our identity to others.
In the most recent publication from the Optical Society, the State University of New York (SUNY) has developed a new biometric scanner that creates a three-dimensional image of finger veins, that claims to have a 99% accuracy.
What is electronic authentication and why is it important?
Electronic Authencation is a way for an electronic system to establish confidence in a user’s identity. With more personal data being stored online, it is important to implement security measures to prevent fraud and identity theft. This video elaborates on the types of electronic authencation.
https://youtu.be/OEVCu1BiO_U
What is biometric authentication and how does it work?
Biometrics are a specific type of electronic authentication, which uses unique characteristics about the individual’s body to confirm their identity. SUNY’s current research falls under physiological biometrics with their focus on blood vessel structures.
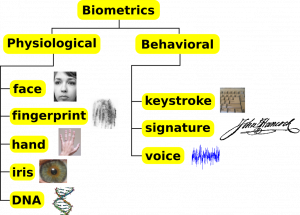
Classification of biometrics under two categories: Physiological (physical traits) and behavioral (patterns in actions) Graphic created by: Alessio Damato
Current hand scanners in the market use ultrasound or optical imaging. Doppler ultrasound uses blood flow in the tissue to determine the location of veins, but is less effective detecting smaller vein structures. Optical imaging has issues with light diffusion in deeper tissue. A mobile scanner can also make images of the dorsal veins in the hand, but these images are 2D and do not account for depth.
To improve biometric authencation methods, it is important to obtain accurate and detailed data for the algorithm to process. SUNY’s hand scanner utilizes photoacoustic tomography. This method relies on the photoacoustic effect, where sound waves are emitted as a result of light absorption, such as from a laser. These waves are then recorded and used to create 3D images. This provides higher quality images because tissues that don’t absorb the light do not emit signals unlike other methods.
The data is put through multiple filters, processed to remove structures aside from the veins, and sent through an algorithm to analyze the structure. This algorithm used to determine the match also has a lower equal error rate (the error percentage where the false rejection and false acceptance rate is equal) of 1.23% compared to other methods.
- 2D vein infrared scanners = 5.6%
- Gait = 7.0%
- Touchscreen = 2.5%
Below is a simplified diagram on the biometric authencation process.
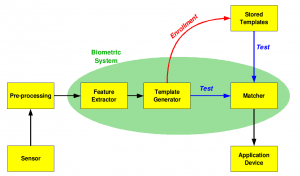
Biometric Authencation obtains data from a sensor, then processes and inputs the data into the biometric system that compares it with the template for a match. Graphic created by: Alessio Damato
Significance of biometric authencation
Biometrics is an alternative method for people who find keeping many passwords for multiple accounts difficult and cumbersome. People with cognitive decline and visual impairment benefit by having secure access to the same services.
With higher accuracy and reliability in biometric authencation, less time could be spent proving our own identity and more time can used for the things we hope to achieve.
–Michelle Huynh
