On Friday, October 30th, Canada reported 3,457 new COVID-19 cases in a single day—a record-breaking number.
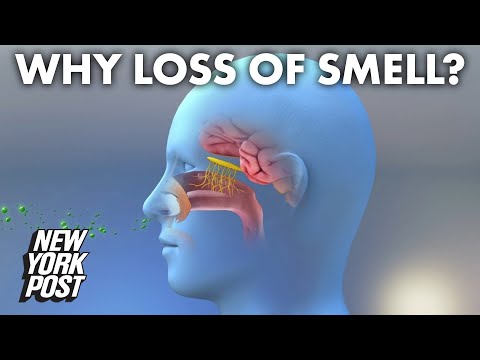
Most people who contract COVID-19 experience mild to moderate symptoms. Although the most recognized symptoms of COVID-19 are cough, fever, tiredness, and difficulty breathing, many COVID-19 patients have reported a loss of smell. Recent research suggests that smell testing may serve as an additional means to identify COVID-19 patients in need of early treatment or quarantine.

Researchers suggest that a sudden loss of smell may be an early indicator of COVID-19. (Engin Akyurt / Pixabay)
How common is the loss of smell among COVID-19 patients?
In a study published in August 2020, researchers analyzed data from over 8,000 COVID-19 patients from 13 countries. Of these patients, around 41 percent reported a loss of smell. It was also found that younger age was correlated with a higher prevalence of loss of smell.
How does COVID-19 cause loss of smell?
Although the underlying mechanisms for loss of smell in COVID-19 patients remain unclear, researchers from Harvard Medical School have identified the cell type vulnerable to infection—olfactory support cells.
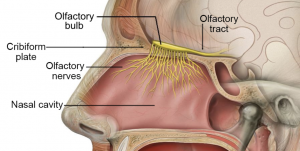
COVID-19 can cause changes within the olfactory system, the sensory system responsible for smell detection. (Lynch / Creative Commons)
The olfactory system is the sensory system responsible for smell detection. Once smells are detected by olfactory sensory neurons, nerve signals are sent to the brain for processing. Findings suggest that the virus infects and causes temporary loss of function of olfactory support cells, which then indirectly causes changes to olfactory sensory neurons. These changes result in the inability for one to process smell.
“I think it’s good news, because once the infection clears, olfactory neurons don’t appear to need to be replaced or rebuilt from scratch,” he said. “But we need more data and a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms to confirm this conclusion,” said Harvard Medical School researcher Sandeep Robert Datta.
Luckily, researcher Sandeep Robert Datta believes that since the virus does not directly affect the olfactory sensory neurons, they are able to regain function over time. Additional research is needed to confirm these findings.
Is the loss of smell a long-term effect of COVID-19?
The majority of COVID-19 patients who have experienced a loss of smell recover their sense of smell within two to four weeks. However, around 25 percent of COVID-19 patients have reported a long-term loss of smell. Due to the novel nature of the virus, the permanence of this remains unknown.
The bottom line
Although not all COVID-19 patients experience loss of smell, sudden loss of smell may be an early indicator of COVID-19. It is suggested that smell testing may be a helpful addition to existing COVID-19 testing protocols. In the meantime, individuals are encouraged to visit a testing site if they exhibit any symptoms, or are concerned that they may have contracted the virus. Individuals are also encouraged to wear a mask, social distance, and limit social interactions with anyone outside their immediate household or essential supports.
Individuals are encouraged to visit a testing site if they exhibit any COVID-19-like symptoms. (Elchinator / Pixabay)
— Alessandra Liu