Dear Team,
The assignment focuses on creating 3 definitions of a relatively complex term in our respective fields to a non-technical audience. The objective of the assignment involves understanding the importance of definitions, and writing the appropriate level of detail. A parenthetical definition, a sentence definition, and an expanded definition are required. The expanded definition needs to contain at least four expansion strategies, one visual, and a minimum of three outside references using APA style.
The Situation
A Computer Science student is explaining the concept of Machine Learning to a non-technical audience. Although the audience is composed of fellow university students, they may not have the technical knowledge about this concept. The students are assumed to have basic computer literacy.
Parenthetical Definition
Machine Learning (mathematical models that use sample data) is a tool that allows computers to make new predictions about unseen data.
Sentence Definition
Machine Learning is a type of technology that aims to mimic human cognition by using past data to make models that can form independent conclusions. These models can help to solve problems for unseen data and can be seen to have multiple real-world applications.
Expanded Definition
What makes it different from Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the study of giving intelligent machines the ability to mimic human cognition and problem solving (IBM Cloud Computing, 2020). AI encompasses many different subfields that make connections between the structure of the brain and computers. Ultimately, these connections are used to give computers the ability to learn information. Machine learning is just another subset of AI that is more focused on the development of mathematical models from data to make predictions and conclusions.
Can Machine Learning be Truly Independent?
Although it may seem like these models are self sufficient, human intervention is required for instances when drastic deviations occur. For example, when the pandemic first began, many of the top suggestions for Amazon’s website changed to toilet paper and wet wipes (Vishnoi, 2020). There are instances where machine learning could be biased toward certain ethnicities, or display the wrong results. Close supervision by researchers is necessary for properly functioning models.
![]()
Figure 1. What’s the Difference Between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning? (Source: Copeland, M “The Official NVIDIA Blog” 2016).
When did Machine Learning begin?
In its earliest years, a scientist from IBM was experimenting with a program that could play checkers against humans (IBM Cloud Education, 2020). He modeled the way that these programs learned after humans, and coined the term “Machine Learning”. Fast forward several decades later, and this technology is seen in everyday use. As the world becomes more reliant on the analysis of data, Machine Learning can help in decision making for several different industries.
How does it work?
At its core, Machine Learning is heavily dependent on data. Computer scientists wanted to transition from explicitly instructing computers, to giving them the ability to learn from past experience and solve complex problems (Bisong, 2019). In order to make these decisions, the computer takes in “training” data (numbers, photos, faces, etc) and then it creates a predictive model. It is then evaluated by giving it some “unseen” data, and then producing results (Brown, 2021). These results are then further evaluated and the model can be tweaked further.
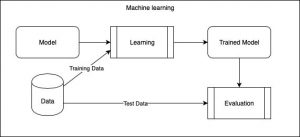
Figure 2. 6 Jars perspective of Machine Learning. (Source: Ramalingam, V “Medium” 2019)
What is it used for?
Machine Learning has several real-world uses (IBM Cloud Education, 2020). One use is for image recognition in a wide variety of settings from hospital clinics, tagging friends on social media, to recognizing handwriting. It is also used in speech recognition to translate speech to a text. Recommendation engines use Machine Learning to curate your Amazon shopping lists, suggest YouTube videos, and arrange your Instagram feed, among many other things.
References
Bisong, E. (2019). What is machine learning? In E. Bisong (Ed.), Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners (pp. 169–170). Apress. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-4470-8_13
Brown, S. (2021, April 21). Machine learning, explained. MIT Sloan. Retrieved September 30, 2021, from https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/machine-learning-explained
Copeland, M. (2016, July 29). The difference between ai, machine learning, and deep learning?: Nvidia blog. The Official NVIDIA Blog. Retrieved September 30, 2021, from https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2016/07/29/whats-difference-artificial-intelligence-machine-learning-deep-learning-ai/.
IBM Cloud Education. (2020, July 15). Machine Learning. IBM. Retrieved September 30, 2021, from https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/machine-learning#toc-real-world-Lyja9GSr.
IBM Cloud Education. (2020, June 3). What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? Retrieved September 30, 2021, from https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/what-is-artificial-intelligence
Ramalingam, V. (2019, February 10). 6 Jars perspective of Machine learning – venkatachalam ramalingam. Medium. https://medium.com/@venkatachalamramalingam/6-jars-perspective-of-machine-learning-35ace2c9442f
Vishnoi, L., 2021. Why Do AI Systems Need Human Intervention to Work Well? – KDnuggets. [online] KDnuggets. Retrieved October 8th 2021. https://www.kdnuggets.com/2020/06/ai-systems-need-human-intervention.htm.
Leave a Reply