Digital Literacies Defined
To understand Digital Literacies we need to start with a definition. The 1990’s saw a rise of research and academics weighing in on this topic. Eager to label this new way of learning, scholars published multiple definitions.
Gilster (1997) suggested digital literacy was “an ability to understand and to use information from a variety of digital sources.” Simply put, it is “literacy in the digital age” (Bawden, 2008, p. 18). The author takes a somewhat controversially, uncomplicated view of this term and states it is now essential for learners to be competent using current technologies.
In 1995, Lanham took a somewhat restrictive view of digital literacy. He determined that a new form of literacy was required to make sense of multiple sources of information (Bawden, 2008). Sources such as text, audio, and images. This definition was criticized for not expanding technology to incorporate any future devices.
According to Bawden, Eshet in 2002 expanded on Gilster’s definition and argued digital literacy is a way of thinking or a specific mindset. To Eshet, digital literacy went beyond competencies and he asserted learners of digital literacy were required to think in a new, technological way.
The last few years (2010 to present) have resulted in the expansion of digital literacy definitions and theories. While scholars and academics continue to research the topic, organizations and institutions have begun to create definitions to fit their educational philosophies or strategic plan mandates. The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has suggested
. . . digital literacy generally refers to a variety of skills associated with using ICT (information and communication technologies) to find, evaluate, create and communicate information. It is the sum of the technical skills and cognitive skills people employ to use computers to retrieve information, interpret what they find and judge the quality of that information. It also includes the ability to communicate and collaborate using the Internet—through blogs, self-published documents and presentations and collaborative social networking platforms.
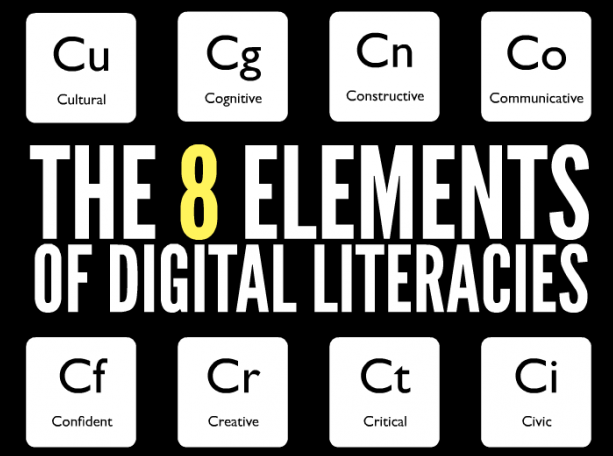
In recognition of the multitude of digital literacy definitions and the ever-changing nature of technology, Belshaw (2012) created a definition which incorporated eight essential elements of digital literacy.
In his doctoral dissertation, Belshaw explores each element:
- Cultural: “the need to understand the various digital contexts an individual may experience” (p. 207)
- Cognitive: “not the practice of using tools, but rather the habits of mind such use can develop” (p. 208)
- Constructive: the creation of an original piece of content through remixing content from other sources
- Communicative: “the nuts and bolts of how to communicate in digital networked environments” (p. 209)
- Confident: “the understanding that the digital environment can be more forgiving in regards to experimentation than physical environments” (p. 210)
- Creative: the ability to complete tasks in a new fashion
- Critical: to observe or reflect on digital literacies contributors and to ask questions based on power structures and assumptions behind digital literacies.
- Civic: “ability for people to use digital environments to selforganise into social movements” (p. 214)
For additional information on Belshaw’s 8 Elements of Digital Literacies, watch the following Ted Talk:
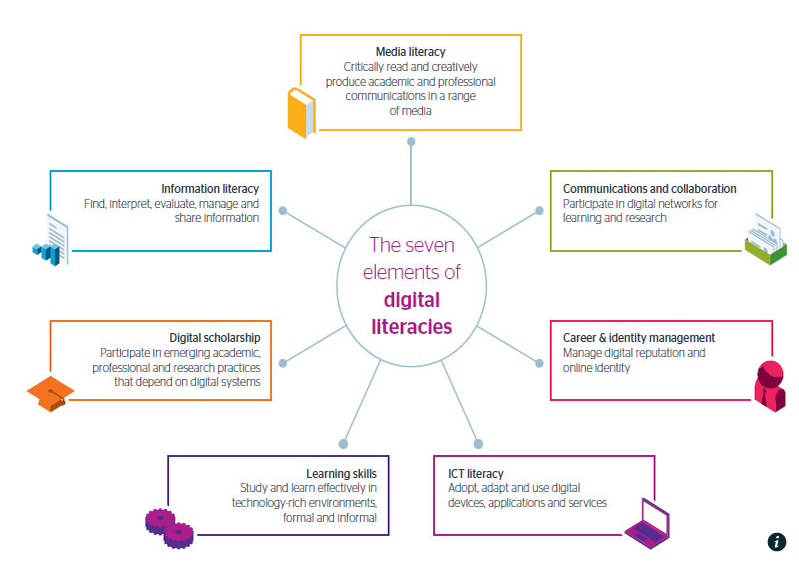
Finally, organizations such as the Joint Information Systems Committee (Jisc) have weighed in on the digital literacy debate. While this organization in the UK focuses on the use of digital technology in education and research, they have expanded the definition of digital literacy beyond that of the FCC. In 2014, they concluded digital literacies are the “capabilities which fit someone for living, learning and working in a digital society”. While this may sound simplistic, Jisc has supplemented their definition with seven elements of digital literacies which learners must embrace in a today’s society.
Jisc incorporated these seven elements to illustrate the complex nature of digital literacies. It surpasses a mindset or a simple uncomplicated definition of using technology and shows a realistic picture of what learners are required to embrace in order to be successful in society.
The evolution of digital literacies has changed over the past 20 years and, according to Belshaw, will continue to change to reflect the nature of technology within society.
References:
albertizeem. (2010). Amazon kindle_24. [Photograph]. Retrieved from https://www.flickr.com/photos/albertize/4506273004/in/photolist-7ScPY9-8pb1o9-9JXa47-7yTvGB-b14bw6-8cV2u9-7ScTzY-8pYgtK-7uTqWv-9fiT3d-eg71xX-eg72Ac-egcJSs-egcFcu-egcKLC-eg6ZAz-egcENE-egcxZw-eg6XLt-eg6ZhR-egcL9h-eg74y4-eg6UyZ-egcGZw-eg6XpR-eg74Yx-eg733e-egcDtL-egcGDG-egcFBJ-eg6SEv-egcBu3-eg6Ske-egcCQQ-eg6TSZ-eg6Tmx-egcyMo-egcNm9-egcA1L-eg6W5t-eg6Y9X-eg71TH-egcxE5-egcz93-9JUk84-9JX9Kf-9JX9Yq-c9guV7-sJVTNP-rN7xcV
Bawden, D. (2008). Origins and concepts of digital literacy. Digital literacies: Concepts, policies and practices, 17-32.
Belshaw, D.A.J. (2011) What is digital literacies? A pragmatic investigations. (Doctoral Dissertation). Retrieved from http://neverendingthesis.com/doug-belshaw-edd-thesis-final.pdf
Belshaw, D.A.J. (2012, March 22). The essential elements of digital literacies: Doug Belshaw at TEDxWarwick [Video file]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A8yQPoTcZ78
Clark, L. & Visser, M. (2011). Digital literacy takes center stage. Library Technology Reports. Retrieved from http://web.a.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.library.ubc.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?sid=f0ee0a73-665a-4a11-a590-ad27953067c6%40sessionmgr4002&vid=1&hid=4206
Joint Information Systems Committee (4 April 2014). The seven elements of digital literacies. Retrieved from https://www.jisc.ac.uk/guides/developing-students-digital-literacy
Joint Information Systems Committee (4 April 2014). Developing students’ digital literacies. Retrieved from https://www.jisc.ac.uk/guides/developing-students-digital-literacy