Topic 1: Personal Learning Environment
A Personal Learning Environment (PLE) is a system that enables individuals to take control of and manage their own learning. It integrates various tools, resources, and strategies to support lifelong learning in a personalized and flexible manner. It includes several key components as follows.
Figure 1. Key Components of a Personal Learning Environment (PLE)
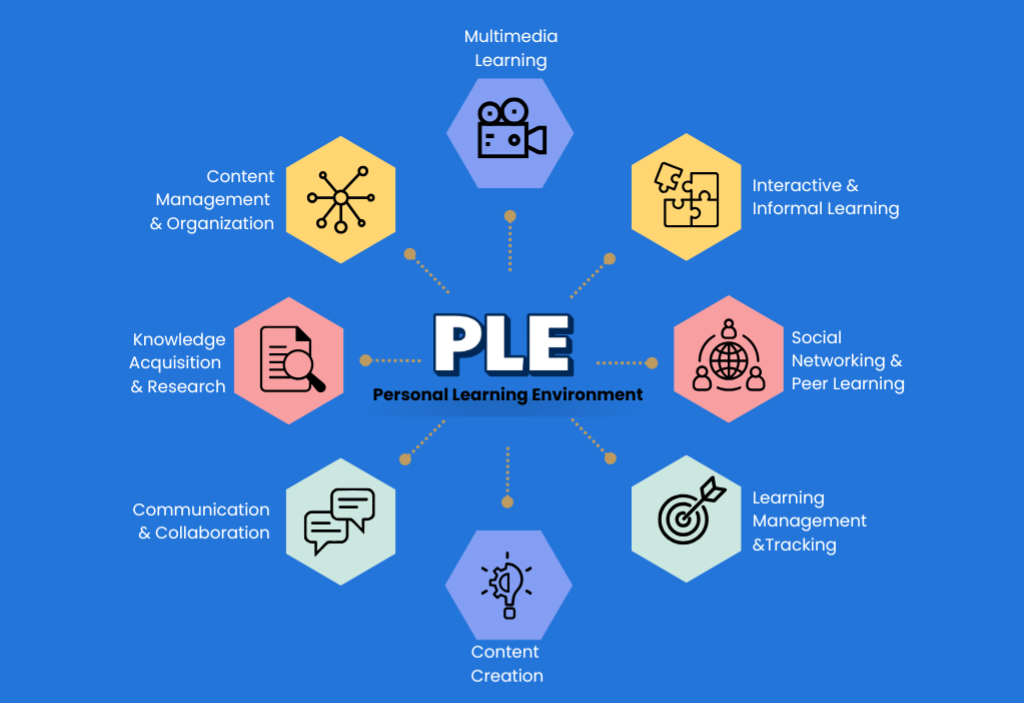
A Personal Learning Environment (PLE) consists of several key components that support individualized learning. Multimedia learning involves utilizing various media formats such as videos, podcasts, and interactive content to enhance learning experiences. Interactive and informal learning encourages self-directed and experiential learning through online courses, forums, and gamified platforms. Social networking and peer learning facilitate knowledge sharing and collaboration through online communities, social media, and discussion groups. Learning management and tracking help learners organize, monitor, and evaluate their progress using digital portfolios, LMS platforms, and self-assessment tools. Content creation enables learners to develop and share knowledge through blogs, videos, and presentations. Communication and collaboration involve engaging in discussions, teamwork, and projects using messaging apps, virtual meetings, and cloud-based tools. Knowledge acquisition and research focus on gathering and analyzing information from academic papers, books, online databases, and expert discussions. Lastly, content management and organization ensure efficient structuring and storage of learning materials through note-taking apps, bookmarking systems, and cloud storage solutions. Together, these elements create a dynamic and adaptable learning environment tailored to individual needs.
A PLE fosters self-regulated learning, adaptability, and lifelong skill development, making it a valuable approach in both formal education and professional growth.
Learning Activity
Based on your understanding of a PLE as described above, click each element to explore examples of relevant tools.
References
Clark, R. C. & Lyons, C. (2010). Three views of instructional visuals. In R. Taff (Ed.), Graphics for learning: Proven guidelines for planning, designing and evaluating visuals in training materials (2nd ed., pp. 15–28). Pfeiffer.
http://ezproxy.tru.ca/login?url=https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/trulibrary-ebooks/reader.action?docID=624441&ppg=37
Schnotz, W. (2022). Integrated Model of Text and Picture Comprehension. In R.E. Mayer & L. Fiorella (Eds.), The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning (pp. 82-99). Cambridge University Press.
https://www-cambridge-org.ezproxy.tru.ca/core/books/cambridge-handbook-of-multimedia-learning/integrated-model-of-text-and-picture-comprehension/984E5EBEFF5D53F5DD8BDA62F6A60718
Ran
February 8, 2025 — 11:15 AM
The learning outcomes for this topic are to understand the meaning of a Personal Learning Environment (PLE), recognize its key components, and identify useful tools relevant to each element. This course is designed to support students as they begin online learning by providing essential information and resources to enhance their learning experience.
In the initial draft of the course notes, the text-only descriptions, including a long list of example tools, felt overwhelming and needed improvements for readability. To facilitate effective information delivery, I created an infographic-style snapshot to summarize key points and enhance visual organization.
This approach aligns with Clark & Lyons (2010), who argue that organizational visuals, which represent lesson structures, can improve learning. Positioned right before the corresponding descriptions, the combination of images and text enhances coherence and contiguity, supporting learning as discussed by Schnotz (2022).
Additionally, I also designed an interactive H5P learning activity integrating the same image to reinforce learning and ensure long-term memory retention.