Experiment Goals
- Which interface encourages users to meet face-to-face more efficiently?
- Which interface allows users to settle on a common interest and plan an event more efficiently?
- Are users more satisfied with Facebook Messenger with the addition of Social Butterfly?
Participants
10 participants will be recruited through convenience sampling of the research team’s network. Participants will be evenly split between those who self-identify as an introvert and those who self-identify as an extrovert. Due to the sampling methodology, it is anticipated that participants will be aged 20-25, currently studying in at a postsecondary institution. This sample is somewhat representative of the target population which is young adults.
Conditions
Two different interfaces will be examined during the course of the experiment, both use Facebook Messenger as the base interface with additional content to change the interface.
Facebook Messenger is a simple chat based interface. It features a list of recent conversations on the left panel, the ongoing message history of the selected chat on the middle panel and information about the current conversation on the right panel. The conversations on this interface will be without any chatbots.
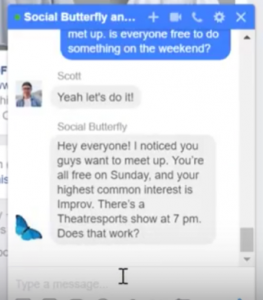
Social Butterfly
Social Butterfly describes an interface of which Facebook Messenger is the base with the addition of a chatbot in all conversations. The chatbot(research team member) will respond to participant entered commands and activate if specific keywords are used during a conversation. The chatbot will recommend events that match all conversation member preferences. This will be triangulated through using the basic and friend profiles provided to the participant and research team respectively.
Tasks
Two, tasks with their order counterbalanced will be completed by the user throughout the experiment. Participants will be given a profile listing their best friends, interests and preferred event types. The pairings of interface and sets of friends will be counterbalanced. Each friend group will have unique interests and constraints. The research team will be operating the other Facebook accounts in the conversation to simulate a discussion. Each Facebook account in the conversations will be assigned a friend profile which details their availability, interests and preferred events. Overall there are four possible combinations of task order and interface order that the participants may get.
Task1: Group Chat
The prompt provided to the participants will be “Use this interface to plan a group outing that satisfies everyone in the current conversation.” The participants goal will be to set up an event within the next week that meets the three other group members contraints.
Task2: One-on-one Chat
The prompt provided to the participants will be “Use this interface to plan a one-on-one outing with your friend in this conversation.” The participants goal will be to set up an event within the next week that meets their friends constraints.
Design
2 x 2 x 2 mixed factorial design, more specifically 2 levels of social classification (Introvert and Extrovert, between subjects) x 2 interfaces (Facebook Messenger and Social Butterfly, within subjects) x 2 tasks (Group chat and individual, within subject)
Procedure
The following details the basic procedure of a participant in our experiment. It should be noted that the order of tasks and interfaces will vary depending on the participant because we will be counterbalancing interface type and task order.
- A preliminary demographic survey will be provided to the participant.
- Participants will be given 3 minutes to read a basic profile and task description.
- Participants will be presented with the SocialButterfly interface. They will be directed to fill out the onboarding flow to record the preferences which have been outlined in the profile provided.
- Participants will then commence Task1 and Task2 on the SocialButterfly interface.
- A followup survey on the SocialButterfly interface will be provided to collect feedback on the user’s satisfaction levels. This will be followed by a 3 minute break.
- Participants will be given 3 minutes to read a basic profile and task description.
- Participants will be presented with the Facebook Messenger interface.
- Participants will then commence Task1 and Task2 on the SocialButterfly interface.
- A followup survey on the Facebook Messenger will be provided to collect feedback on the user’s satisfaction levels.
- The participant will fill out a closing survey to gather their preference on the interface and their overall satisfaction with both Facebook Messenger and SocialButterfly.
Apparatus
The experiment will take place in various project rooms in ICICIS. The participant will be presented with each interface on a provided laptop with the basic profile and task prompts on a separate piece of paper for their reference.
Independant and Dependant Variables
The dependent variables of the experiment are as follows:
- Time to Completion – How long from when the participant beings the conversation measured until all conversation members agree on a specified event plan. A research team member will record start/stop times in a spreadsheet.
- Error – Recorded each time an individual in a conversation declines the proposed event. The chat log of the conversation will be reviewed to identify any errors which will be segmented by task and interface type.
- User Satisfaction – Recorded based on a likert scale (converted to continuous data) that seeks to understand their satisfaction with each interface after completing both tasks. The participant will fill out their preferences in the Interface surveys following the completion of both tasks.
The independent variable of the experiment are as follows:
- Social classification (Introvert and Extrovert, between subjects)
- Interfaces (Facebook Messenger and Social Butterfly, within subjects)
- Task Type (Group chat and individual, within subject)
We will be controlling for the various variables:
- Order of Tasks – The order that each participant completes the assigned tasks will be counterbalanced.
- Order of Interfaces – The order that each participant sees each interface will be counterbalanced.
Hypotheses
Efficiency
- H1: Participants who use Social Butterfly for Task 2 will be faster and have fewer errors.
Null: Participants who use Social Butterfly for Task 2 will perform the same as users on Facebook Messenger. - H2: Participants who use Social Butterfly for Task 1 will be faster and have fewer errors.
Null: Participants who use Social Butterfly for Task 1 will perform the same as users on Facebook Messenger.
Participant Satisfaction
- H3: Introverts will be more satisfied with Social Butterfly than Facebook Messenger.
Null: Introverts will demonstrate no difference in satisfaction between Social Butterfly and Facebook Messenger. - H4: Extroverts will be no less satisfied with Social Butterfly than Facebook Messenger.
Null: Extroverts will be less satisfied with Social Butterfly than Facebook Messenger.
Statistical Analysis
An Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) will be used to the test the difference in means between time, error rate and satisfaction level. Ordering of interfaces and tasks will also be considered as a potential confounding factor.
Limitations
Various limitations exist due to the limited resources and small scope of this experiment. The group conversation scenarios are very forced, unnatural and thus, not very representative of typical interactions. Due to using Facebook Messenger, the research team has no way to measure conversation variability which could prove to be a valuable variable in the future. The experiment only considers one possible alternative to Social Butterfly, Facebook Messenger, whereas other interview participants noted their use of WhatsApp and WeChat. Considering that the participants don’t end up going to the event and rating it, it is hard to fully visualize the impact of having an event that meets all conversation member constraints. The scope of this experiment does not permit exploring social burnout, but the research team suggests future research should be conducted to develop potential evaluation methods.
Supplemental Experiment Materials
- Preliminary Demographic Survey
- Basic Profile, Friend Profiles, Task Write-up
- SocialButterfly Commands