Many scientists commonly believe that it must be beneficial for bacteria to incorporate DNA sequences into its own genome. They believe that this process of acquiring the DNA from the environment exists to make new random combinations of genes. These new combinations would replace the genes currently residing within the cell. However, Dr. Redfield did not simply accept this theory to be true; she began to question exactly what the purpose behind this process is. To her, the idea that the bacteria would take up genes lying around in the environment is not probable. One possible explanation is that the foreign DNA is left behind by dead cells; thus, they are unlikely to be useful. Dr. Redfield proposes that regardless of whether the DNA uptake will be beneficial to the bacteria or not, the accumulation of the DNA sequences in the cell would still occur.

Dr. Redfield hypothesized that the bacteria were either making new combinations of the genes by accident or it could have been a side effect from another important process. Nevertheless, Dr. Redfield believes that the bacteria uptake DNA for food, which is a radical idea for many scientists.
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
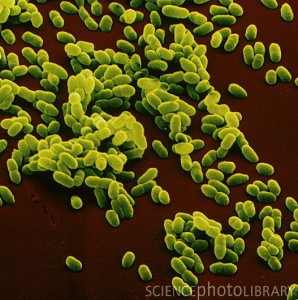
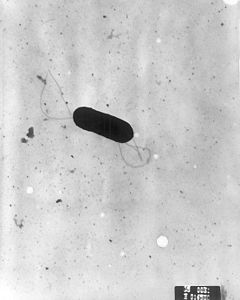
To test her theory, Dr. Redfield needed to choose a type of bacteria that were “picky eaters.” Most bacteria do not have a preference for the DNA sequences that they uptake. However, she found two unusual types of bacteria that turned out to be picky eaters: Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrheae. They both have a preference for the specific sequences of the DNA that they will accumulate; and these chosen sequences are similar to their own.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LoQ16P0K4b0&feature=g-upl
How is Dr. Redfield’s research relevant to you?
Her research probably will not impact you drastically in your daily lives, but that does not mean that it will never affect you in the future. Scientists are now interested in how and when bacteria are able or unable to reproduce. Once they discover the types of DNA the bacteria eat and how they acquire their food, scientists will be able to control their growth.
Further research on this field will prove to be very essential for medical purposes.The knowledge of how bacteria work is crucial to humanity. Bacteria are all around us and they deserve our time for they can be beneficial, and yet harmful to our society.
Interviewee: Dr. Rosemary Redfield
Narrated by: Hanna Oh, Cha Tumtaweetikul, Jacyln Wiebe, Steven Xian
Soundtrack credits to: suonho, Puniho, FreqMan, mansardian, BristolStories, digifishmusic, milton. and Setuniman.
Editted by: Steven Xian
Equipment and advices: Bruce Dunham, Eric Jandciu, Jackie Stewart, Andrew Trites from SCIE300.
Resources:
We would like to thank Dr. Rosemary Redfield for her interview and her Uptake Video animation and also the SCIE300 professors and teaching assistants: Bruce Dunham, Eric Jandciu, Jackie Stewart, and Andrew Trites for their advice.