Let’s face it, you’ve probably never heard that saying before. Apart from having a good time and feeling great in the moment, alcohol consumption is generally associated with a negative connotation. Recent studies have shown that moderate drinking can increase a person’s life by dropping their risk of early death by 18%. Although studies have associated drinking with some health benefits, it is more commonly known as being addictive and highly toxic. Even with this common knowledge, millions of people globally continue to consume alcohol on a daily basis, and thousands of alcohol-related deaths occur annually in the United States.

Shots of hard alcohol. Source: Flickr Credit: Kirti Poddar
BUT THEY SAID IT WAS GOOD FOR YOU…

Pouring a glass of red wine. Source: Flickr Credit: Rawpixel Ltd
New research has found that moderate levels of drinking, defined as one or two glasses of wine or beer per day, can be linked to a longer lifetime. People who consumed alcohol were less likely to die due to cardiovascular disease than those who did not. Red wine was also found to have some anti-aging benefits associated with it, due to the presence of antioxidants. A 2017 study that excluded non-drinking participants with other health issues and addiction once again found a correlation between those who consumed alcohol and a lowered risk of heart attacks, chest pains, strokes, and fatal heart disease. In addition, it has been found that moderate drinking can reduce insulin resistance, which is the primary cause of type 2 diabetes. Although these findings may seem promising to many, no direct cause and effect has been found between moderate alcohol consumption and longevity.
WHAT’S IN IT?
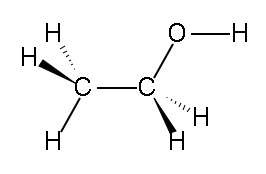
Line-bond structure of ethanol (CH3CH2OH). Source: Wikimedia Commons Credit: Sevela.p
The main ingredient in alcohol that is responsible for getting people “drunk” is ethanol, a psychoactive molecule that impacts the central nervous system, altering brain function and hence causing visible changes in mood, behaviour, perception, and consciousness. It is produced by the yeasts that digest sugars in foods such as grapes and grains that are used to make wine and beer, respectively. When alcohol enters the bloodstream, “pleasure hormones”, known as endorphins, are released and transported to the brain where, over time, they are able to shrink the part of the brain that is responsible for memory and reasoning. In red wine specifically, the presence of the compound resveratrol contributes to the antioxidant-like benefits of drinking.
FAKE NEWS

Ambulances parked at the emergency entrance of a hospital. Source: Flickr Credit: Can Pac Swire
Data from 2006 to 2010 taken from the Centre for Disease Control’s (CDC) Alcohol-Related Disease Impact (ARDI) online application shows that 88,668 alcohol related deaths occurred in the United States within those four years. Of those deaths, 44% of them were due to chronic causes, primarily liver disease, and the remaining 56% were from acute causes, including motor-vehicle accidents and suicide. Overall, it was found that males accounted for 71% of alcohol-related deaths. People in the 50 to 64 age cohort contributed the greatest quantity of alcohol-related deaths. These statistics show that although there are indeed some health benefits to alcohol consumption, alcohol should continue to be consumed only when safe, and most importantly in moderation.
Written by Kelsey Wong

2 responses to “A Shot a Day Keeps the Doctor Away?”