Among all human organs, the brain is the most important and complex. The brain is the organ that regulates the function of the body and is the material basis for advanced neurological activities such as consciousness, spirit, language, learning, memory, and intelligence. The brain needs a nervous system to perform these neural activities.
In short, the nervous system is an intermediary that can transmit messages from the brain to various parts of the body. Neurons are the basic unit in the nervous system and they communicate through synapses. Synapse is like a bridge between nerve cells, and there are more than 100 trillion synapses in a typical brain. The formation of synapses is essential to ensure a nervous system can function smoothly since the number of synapses is very large.
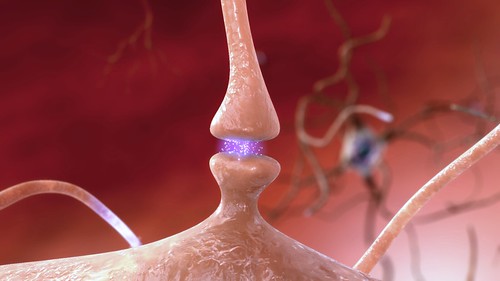
(One synapse in the nervous system. Source:Flickr.)
In 2018, Chen and his research team did a study about how the nerve cell formation of a worm, which is called C. elegans, is affected by one protein called Plexin. In this study, they found that two genes (Rap2 and TNIK) regulated by Plexin can affect synaptic tiling of C. elegans, and synaptic tiling is one kind of synapses formation. That is increased activity of Rap2 holds up synaptic tiling and TNIK is the opposite. The following video describes the story of their research.
Their findings are very helpful for other neuroscientists to understand the role of these genes in synapses formation. According to Ethan Fortes, one of Chen’s research team, “What we hope to do is to provide a deeper understanding of the function of the genes that might be disrupted in people who have neurological differences or disorders.” This study can be a very good inspiration for future study on other species whose nervous system is more advanced and more structurally related to humans.
The podcast below involves a conversational dialogue with the researcher and he answered some general questions from the perspective of researchers.
Studying the brain and nervous system is of great significance to humans. Brain and nervous system problems are quite common and more difficult to prevent. Beyond that, problems with the nervous system were found to be the cause of some mental illness such as Autism.
Group 2
Nathan Yan, Fareez Sanif, Zijie Lin, Serena Yu