VIRTUAL REALITY
The purpose of this assignment is to understand the precision necessary for definitions in the professional setting as there can be many representations or meanings in many different fields. This assignment aims to build effective communication in explaining definitions by composing three types of definitions (parenthetical, sentence, expanded) for a relatively complex term.
Situation / Audience:
The following term is being described to a group of students of the English 301 Technical Writing class with general working knowledge of basic computers and technology. This will be a non-technical explanation of the term “Virtual Reality” for fellow peers. To understand Virtual Reality and its purpose, readers will need an overview of what it is, how it came to be, its operation, and applicational uses.
The audience will have little to no knowledge on the technological software and hardware components that fully operate to make the virtual reality device run, which would include CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) processors. It simply portrays the big picture outlook of virtual reality and its potential applications in computer technology for the readers.
Parenthetical Definition:
Users can use computer technology to create or access virtual reality (an artificial environment experienced through sensory stimuli).
Sentence Definition:
Virtual Reality is a computer technology with specific hardware and software components that builds a computer-generated environment through immersive head-mount displays. It recognizes user movements to provide a three-dimensional experience that seems very similar to reality.
Expanded Definition:
(Sentence Definition, Etymology, History, Visuals, Operating Principle, Examples)
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality is a computer-generated simulation of a three-dimensional image or environment in which users can interact with it using electronic equipment such as a head-mounted screen or handheld controllers.
The term “virtual” has been used in the computer sense to mean “not physically existing but made to appear by software”. Virtual reality is now recognized with the help of Jaron Lanier in the 1980s through their development of gear needed to experience what he described as “virtual reality”.
 Figure 1. Oculus Rift Virtual Reality Headset
Figure 1. Oculus Rift Virtual Reality Headset
(Source: Oculus Rift CV1, Wikipedia Virtual Reality Headset)
 Figure 2. Head-Mounted Display Graphical Image Rendering
Figure 2. Head-Mounted Display Graphical Image Rendering
(Source: Oculus DK2, Wikipedia Virtual Reality Headset)
The common gear used to experience virtual reality can be seen in Figure 1 which is the typically used headset that creates the near reality experience. The technology from these headsets is shown in Figure 2, in which there are separate LCD screens that render its images for each eye.
What is its history?
 Figure 3. View-Master Type Stereoscope from the 1900s
Figure 3. View-Master Type Stereoscope from the 1900s
(Source: Cooper Hewitt, Through the Looking Glass)
Early research by Charles Wheatstone, demonstrated that the human brain could process two different two-dimensional images from each eye into a single image of three-dimensions. Placing these two images side by side would allow the viewer to simulate a sense of depth and immersion from these two-dimensional images. This led to the development of a popular View-Master Stereoscope device designed for the use of “virtual tourism” as shown in Figure 3.
 Figure 4. Sensorama Machine
Figure 4. Sensorama Machine
(Source: The Sensorama: One of the First Functioning Efforts in Virtual Reality, History of Information)
Another early implication of virtual reality revolved around the idea of developing a simulated environment. A machine known as the Sensorama shown in Figure 4, was developed by Morton Heilig in 1956 and was designed to allow individuals to experience the feeling as if they were in a movie. The device would simulate a near reality experience in which an individual could ride through a city on an imaginary motorcycle with triggered elements that stimulated senses such as the vibration of the motorcycle using a motional chair, the smell of the motor’s exhaust using odor emitters, and the wind blowing past your face from fans.
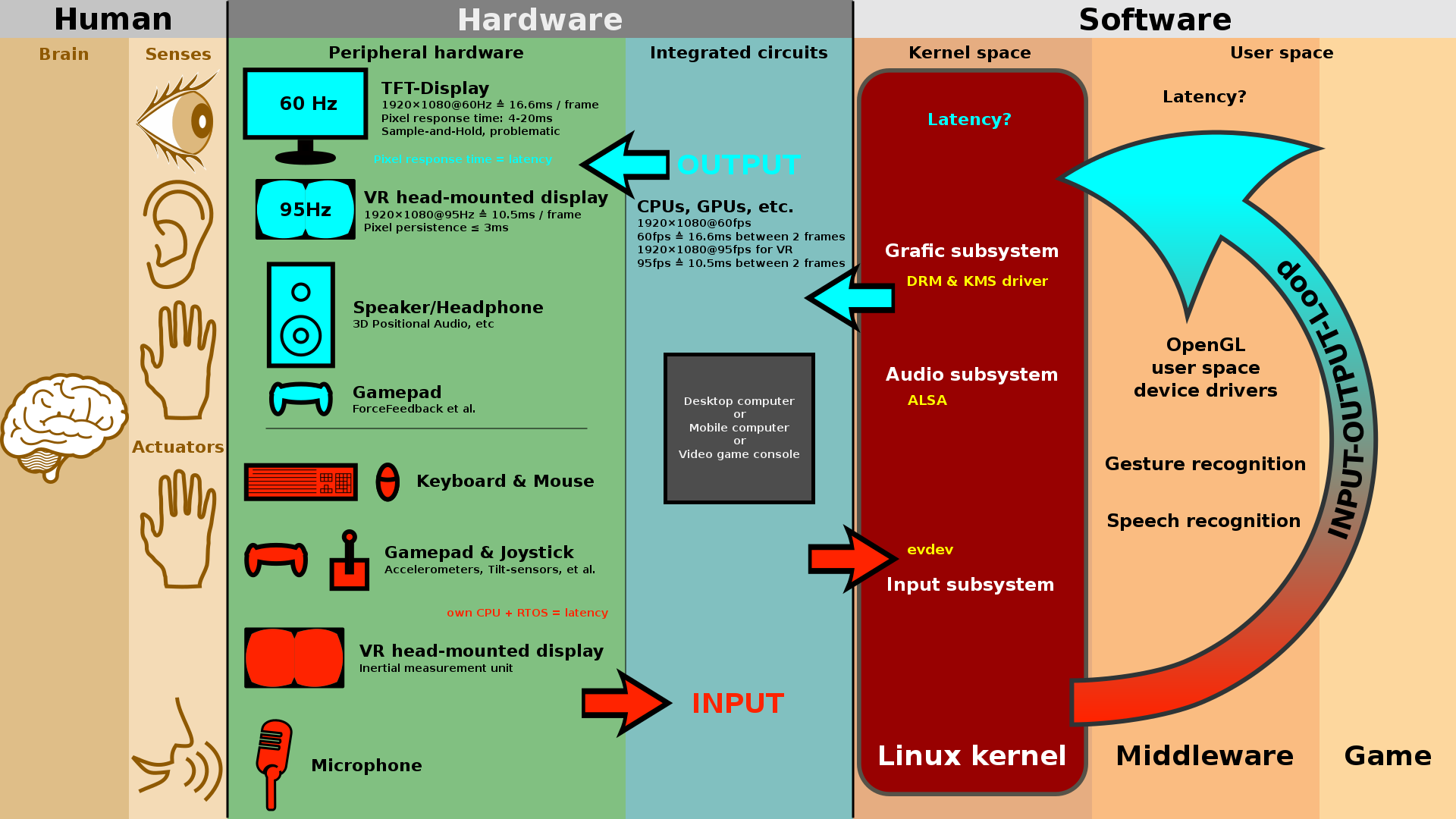
Figure 5. The interactions of hardware and software components on the user in virtual reality
(Source: The input/output loop: Human Machine Interface, Linux kernel and gaming input-output latency, Wikipedia Virtual Reality)
The system of input and outputs can be seen represented in Figure 5, which illustrates the type of human senses that can be manipulated upon in virtual reality. The link between these human senses can be seen through the corresponding components of hardware and software that loop between the recognized input and output responses.
How does it work?
For an individual to experience virtual reality, it would require a head-mounted display which is a virtual reality headset designed like a pair of goggles fixed with monitors to provide separate images for each eye. Virtual reality works in the hardware end to produce stimuli that manipulates the user’s senses. It operates by using sensors to track motions given by the user which could include button presses on a controller or body movements. These inputs are then converted into an electrical signal that is fed into the hardware device to produce a high-quality graphical rendering of the display content or environment to the user to generate a feeling. The software behind it manages both the input and output signals of the device, such as to generate the correct feedback response.
What are the potential applications?
Virtual reality is commonly used in the entertainment industry for applications such as video games, 3D cinemas, and the creation of virtual worlds. Virtual reality is seen as a consumer product in this field and is leads itself as a product for user experience.
However, virtual reality can be applied to the field of education and training such that it provides the opportunity to develop skills without the risks and consequences of the real-world. This approach of virtual reality training can be seen best in the form of flight simulators which uses the application of virtual reality. Similarly, it can be an useful application in the medical field in jobs like surgeons. Through virtual reality, surgeons can implement practice procedures without the need of an operating room and also remove the death consequences.
With the understanding that virtual reality can impose certain senses, virtual reality can be incorporated as a tool in the field of social and psychological sciences as well. It has the ability of altering perception, emotions and physiological states in a controlled environment which can be used to study specific interactions of interest. These applications of virtual reality can be an important factor to future research and further understanding in many fields.
Works Cited
“Education and Training.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., https://www.britannica.com/technology/virtual-reality/Education-and-training.
“History of Virtual Reality.” The Franklin Institute, 19 Dec. 2019, https://www.fi.edu/virtual-reality/history-of-virtual-reality.
“History of Virtual Reality.” Virtual Reality Society, 2 Jan. 2020, https://www.vrs.org.uk/virtual-reality/history.html.
McFadden, Christopher. “History of Virtual Reality.” Interesting Engineering, Interesting Engineering, 12 June 2020, https://interestingengineering.com/whats-in-a-name-the-long-and-short-history-of-virtual-reality.
Steuer, Jonathan. “Defining Virtual Reality: Dimensions Determining Telepresence.” OUP Academic, Oxford University Press, 7 Feb. 2006, https://academic.oup.com/joc/article-abstract/42/4/73/4210117?redirectedFrom=PDF.
“Virtual Reality Applications.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 23 Sept. 2021, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_reality_applications.
“Virtual Reality.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 29 Sept. 2021, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_reality.
“Virtual: Search Online Etymology Dictionary.” Index, https://www.etymonline.com/search?q=virtual.
Leave a Reply