Everyday we are constantly surrounded by different types of screens. For example: our computer screens, our TV screens, and our cell phone screens. However, the images we see are not comparable to what we see in reality. Being aware of such a difference can be dissatisfying, especially when we look at pictures of: the sunset, the mountains, and the beach. Jakob Emmel, a Ph.D Candidate from the Physics Department at the University of British Columbia, was not an exception.
The first time he saw high dynamic range (HDR) displays that can show huge contrast, he described it as an “eye-opening experience.” HDR refers to the ratio of the maximum darkness to the maximum brightness that a screen can show. The higher the ratio, the better we can distinguish the “black” parts of the screen compared to the “white” parts. For comparison, a common non-HDR display may show a contrast ratio of 1000:1 while average human eyes can see a contrast of 100,000:1. HDR displays can show a contrast in the range of the human eyes or even higher.
Nonetheless, there are still drawbacks with these awesome displays. In the video below, Jakob describes how current displays can be improved in projecting more uniform brightness across the screen as well as the contrast:
Although Jakob’s research was successful, the first prototype he made was not as effective. To control the light coming from each light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for better contrast and uniformity, he had used black filters on top of each LEDs. However, due to the nature of these filters, they absorbed some of the light rather than allowing the light to brighten the screen.
In his second prototype, Jakob made white filters with special reflective coatings. This allowed the spreading light from each LEDs to be reflected back to its source rather than be absorbed, preserving the light more efficiently. This way, dark areas can be dark and bright areas can be bright in the displays.
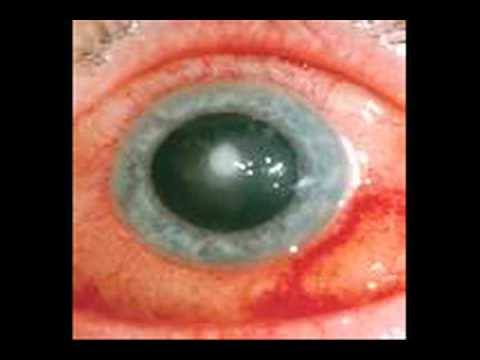
This technology can be applied in many areas. The most prominent source for its effective use is in medicine. With a better display, doctors can see images more clearly and be able to differentiate them more effectively since even the smallest irregularity can be a sign of a deadly tumor.
Specified in the podcast is the technology’s application in movie post editing. As doctors could examine x-ray or MRI images better, movie editors can take advantage of this as well for spotting inequalities in the raw footage.
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
It is adequate to say that Jakob Emmel’s technological innovation is a step forward in grasping reality into the pocket screens of our phones and more. Contribution in the fields of medicine and movie production may only be the tip of an iceberg of vast technological advances to be uncovered.
Group 1
Jina Choi, Matthew Hong, and Angelica Reyes