Double Rainbow Song by Paul Vasquez and the Gregory Brothers.
Source: Youtube channel (schmoyoho)
You may have heard of the “double rainbow song,” in which a man named Paul Vasquez ecstatically reacts to seeing a double rainbow. Now imagine Vasquez’s excitement when he finds out that a quadruple rainbow does indeed exist, and was just recently captured on camera for the first time by German meteorologist Michael Theusner. His findings were published in the October 1, 2011 issue of the Applied Optics journal.
Rainbows form from the refraction of light. Source: Wikimedia Commons
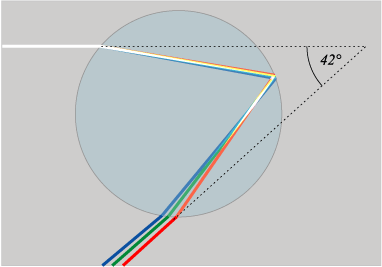
Rainbows are formed by the refraction of light through water droplets in the air. This refraction sometimes occurs a second time after being reflected once in the droplet to form a double rainbow. Rarely does the process occur inside the water droplet a third or fourth time for a triple or quadruple rainbow.
Sightings of triple and quadruple rainbows are extremely rare, as the conditions needed for them to form are increasingly more difficult (only a small portion of the light rays are reflected for a second refraction, and even smaller for the third and fourth refraction). Due to the drastic decrease in intensity, triple and quadruple rainbows are nearly invisible to the naked eye, and require image editing to be able to be seen. Additionally, the third and fourth rainbows can be easily missed because they are located away from the first and second rainbows.
Original and digitally enhanced pictures of the triple and quadruple rainbow. Source: Michael Theusner
The discovery and photography of triple and quadruple rainbows contributes to more than just another Internet meme. In addition to being a scientific breakthrough, it is also a reminder for all scientists to be meticulous and detailed when making and recording observations, as there can be more contributing factors and things going on in a particular experiment than what’s immediately visible. Much like how a series of image manipulations was required to see the additional rainbows, a detailed and thorough analysis of data could lead to discoveries that might not otherwise be found.