There was Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster on March 15th 2011 which released radioactive materials due to equipment failures and nuclear meltdown. Concern remains over the potential effect on human health from radiation leaks at the stricken Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant.
What is radiation?

Radiation is a process in which energetic particles or waves travel through a medium or space. The energy comes from a source and travels through space and may penetrate various materials. Iodine and cesium are examples of radioactive elements. There are two types: ionizing, and non-ionizing. Both types can be harmful to organisms while ionizing radiation is more harmful as it can cause DNA damage.
We are all naturally exposed to background radiation from radon (Rn), colourless, odorless chemical gas found in soil, water and air. We are also exposed to unnatural sources such as X-rays which deliver about 10days’ worth of naturally occurring radiation.
Symptoms

Symptoms of radiation sickness occur when the body is damaged by a very large dose of radiation over a short period of time. The more radiation a person absorbs, the sicker one will get. The best way to prevent harm is to prevent exposure. The strength of the radiation itself and distance from it are key factors in the severity of radiation sickness.
Nausea and vomiting often begin within hours of exposure, followed by diarrhea, headaches and fever. Since radiation destroys infection-fighting white blood cells, the greatest short-term risk after exposure is infection and the spread of infectious diseases.
Human impacts
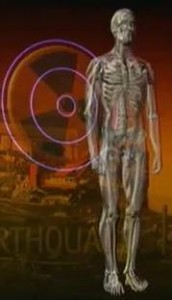
Ionizing radiation damages the body’s internal chemistry. Our bodies are able to repair effects of radiation on tissues, but too much radiation can cause DNA damage that the body can’t repair, leading to cancer.
Vulnerable areas include:
- -Thyroid gland
- -Bone marrow
- -Cells lining the intestine and stomach
Babies and young children are more sensitive to radiation exposure because their cells typically divide faster than adults; increasing their risk of developing a radiation-related cancer later in life.
Treatment
Drugs can stimulate the growth of white blood cells and help people fight off infections. Exposed individuals can also be given capsules containing a dye that binds to thallium and cesium and helps the body get rid of these radioactive elements.
Potassium iodide tablets are often given out to people at risk of contamination. The compound prevents or reduces absorption of radioactive iodine, through the thyroid gland, which uses iodine to produce thyroid hormones. But potassium iodide cannot prevent radioactive iodine from entering elsewhere in the body and does not affect the absorption of other radioactive elements, such as cesium, which stays in organs, tissue and the environment much longer than iodine.
We must watch out our nuclear plant cells since one disaster may cause series of problems. There are many nuclear plants that can potentially become problems and we should find ways to minimize or avoid further disasters.
 but let’s face it and allow me to ask, what have we done with the extra hour? With all the assignments and projects from different courses, social events with friends, schedules working times, most of us probably were not in our bed, sleeping.
but let’s face it and allow me to ask, what have we done with the extra hour? With all the assignments and projects from different courses, social events with friends, schedules working times, most of us probably were not in our bed, sleeping.






