Sleep is a universal behavior for many species on earth. Almost all mammals spend a fair amount of time sleeping every day. Adult humans, specifically, normally spend eight hours per day sleeping, and most of us will sleep over 175,000 hours in our lifetimes. Imagine how much more we could have achieved if we don’t have to sleep. Therefore, it is pretty intuitive to ask the question, do we need this much sleep? This famous study of sleep reduction may give the answer.
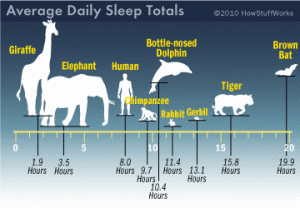
Average Daily Sleep Totals of Different Animals (credit: @HowStuffWorks)
In 1977, Freidman et al. conducted a long experiment based on a gradual sleep reduction. During the study, participants were asked to gradually reduce their nightly sleep until they reached 6.5 hours per night. Then, the participants were asked to reduce their nightly sleep further until they no longer desired to reduce their sleep. The shortest duration of sleep was maintained by the participants for one month, and for the following two months, a sleep duration of 30 more minutes was allowed for each participant. The health of participants were recorded throughout the experiment.

Sleep Reduction/Deprivation (credit: smallbusiness.uk)
After sleep reduction for such a long period of time, we would expect to see a reduction in participants’ physical and psychological health. However, contradict to our common sense, although all of the participants display an increase in daytime sleepiness after they have reduced their sleep below 6 hours per night, there was actually no change in their mood, physical healthy or performance on tasks of vigilance or memory. Overall, their daytime activities were not influenced by the long-term sleep reduction.
The most interesting part of this study is probably that multiple participants reported daytime discomforts and reduced performances at work or school, although their performance was not actually influenced based on objective/physical measures. For example, some participants felt more distracted, depressed and sick (symptoms like having a cold) during sleep reduction, but when they were asked to perform tasks that require attention and efficiency, there was no noticeable change.

Feeling Sick (credit: Aleksandra Sabelskaia)
Return to our original doubt, do we have to sleep as much as we do now? Based on this famous example, if subjective feelings were set aside, the answer is probably no. Sleep reduction only has a minimal impact on one’s performance during daytime, probably because that sleep deprivation increases the efficiency of sleep as recent researches have shown. However, more profound influences of sleep reduction and the physiological basis behind may need more studies for us to safely reduce the amount of sleep.



