Category — 2.7 Children who are Chronically Ill: Diabetes
Children with Diabetes
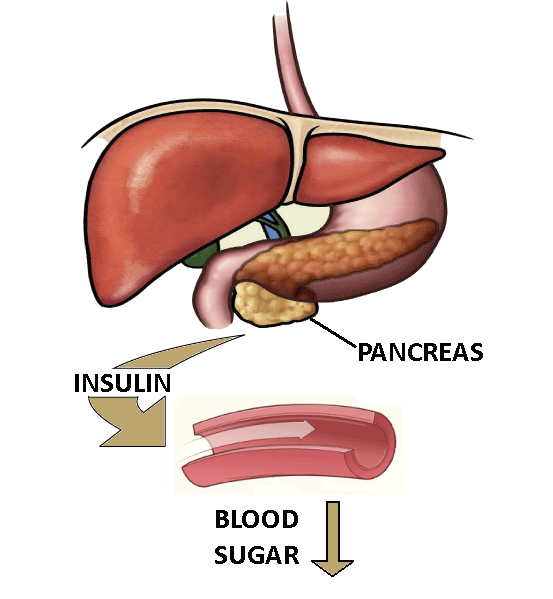
Diabetes1 is a condition in which the body either does not produce enough insulin (see full Glossary) or does not use the insulin effectively (Fig.1 ).
Figure 1. Diabetes
Early Symptoms can include:
- frequent peeing in large amounts
- frequent thirst
- dry mouth or throat
- weight loss
- increase in appetite
- feeling tired, drowsy, or weak.
Another symptom in toddlers or infants includes having a diaper rash that doesn’t improve with medicated cream.
More serious symptoms may appear if the diabetes is not treated, or in some cases when it is undiagnosed. For example a child may have stomachaches, severe nausea and vomiting and heavy, rapid breathing.
There are two kinds of diabetes that a child can develop: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 2 diabetes is linked to obesity. This is when children rapidly gain too much weight. To learn more about diabetes Types 1 or 2 in young children, click on Children-with-diabetes.
Treatment and other Interventions
The first step for children with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes is to understand how to use insulin or insulin dosing. Because the child’s body either can no longer make insulin, or cannot use it the right way, it must be replaced throughout the day, usually by injecting it.
These are vital steps to follow:
-
- Test the level of sugar in the blood, or blood glucose testing at mealtimes and bedtime;
- Know how to manage low levels of sugar, or blood glucose levels, a problem for kids with type 1 diabetes;
- Eat right. A dietitian or nutritionist can help suggest the foods that help avoid changes in the level of sugar in the blood;
- Exercise regularly to maintain a lower level of sugar in the blood. Parents will need to check their child’s blood glucose levels before and after exercise.
To learn about diabetes in the middle childhood years, please visit the six to 12 part of this course.
1 see References
January 31, 2011 No Comments