The status of libraries in California has been pretty grim over the last decade. Budget cuts, the rising recession and unemployment rate have had a tremendous impact on state, county, and city libraries in California. A recent article in Education-Portal.com, “Libraries in Crisis: What Budget Cuts Mean for CA Libraries” by Meghan Driscoll summarizes that “Since the early 2000s, over 75% of funds for the programs listed above have been eliminated. This latest round of cuts will mean yet another loss of library staff, a potentially deep reduction in library hours and limited availability of books and other materials.” According to a Library Journal article by Michael Kelley the budget cuts will lead to a collapse of a 30-year-old resource-sharing network, such as interlibrary loan services. Whether or not such decisions constitute a “shock and awe” budgetary approach, the goal of which “is to inspire middle class voters to come out in June to vote for a revenue-raising ballot proposal,” as Driscoll states, is ultimately beside the point. What does matter is how California’s libraries will be able to maintain certain levels of services.
Some of you may recall an earlier 2004 California public library crisis, the closure of the Salinas public libraries. Here is an American Library article by Pamela A. Goodes and an ALA 2004 press release that presents a refresher. Lots of changes have happened to the Salinas Public Libraries since 2005. With the help from private contributions and the passage of a local tax measure, the library now features a Digital Arts Lab (as of 2007), a Bookmobile (as of 2009), as well as a new and improved web interface. Whether or not the state of California will rally to the aid of libraries, schools, and universities, is a discussion that is beyond the scope of this entry. However, as a former Californian, I find the issue of what sorts of services are available or provided through local libraries to be of particular interest.
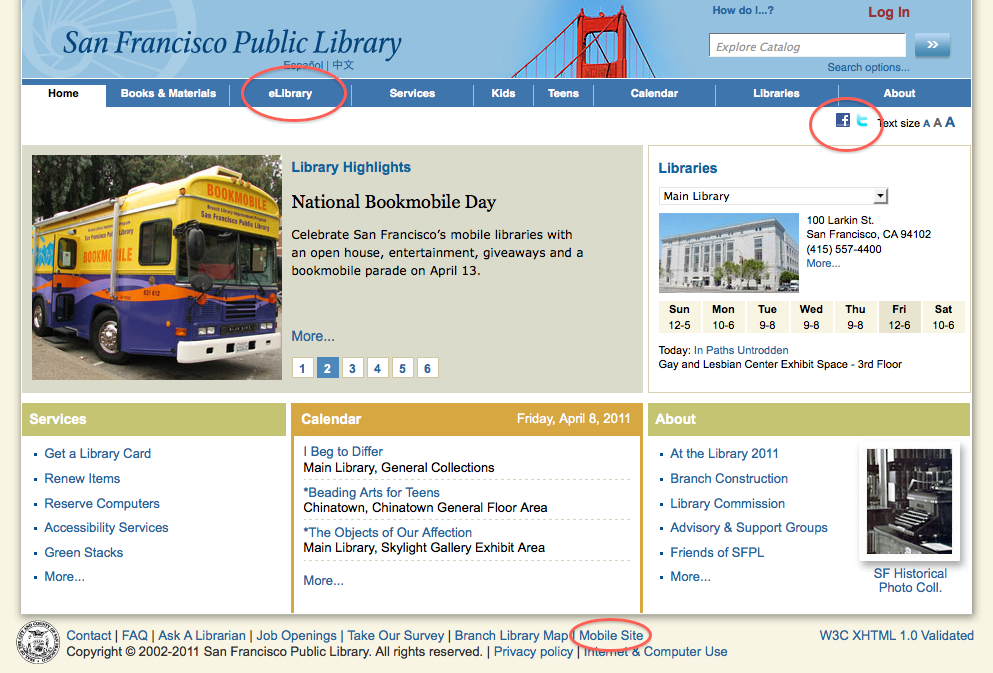
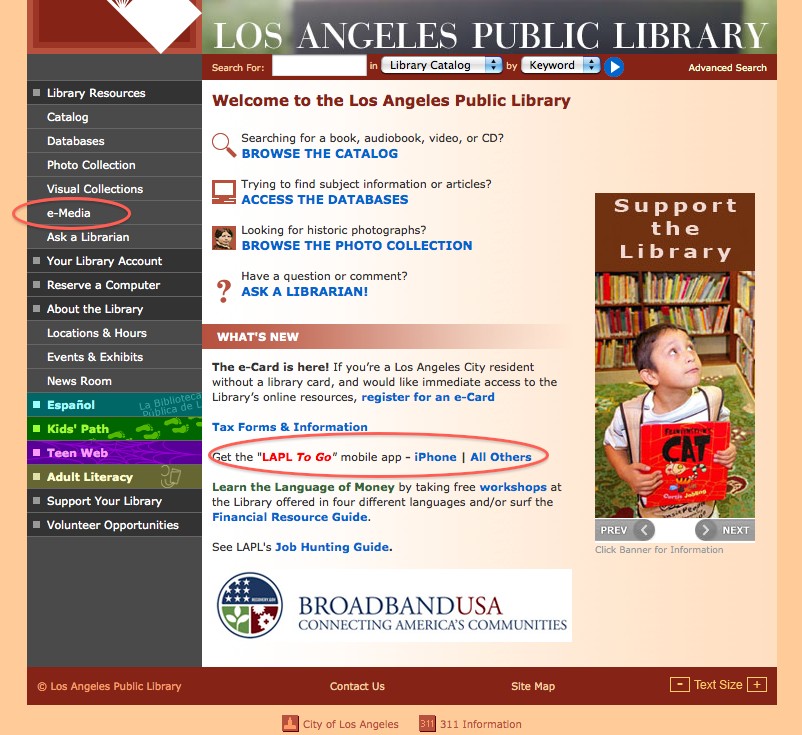
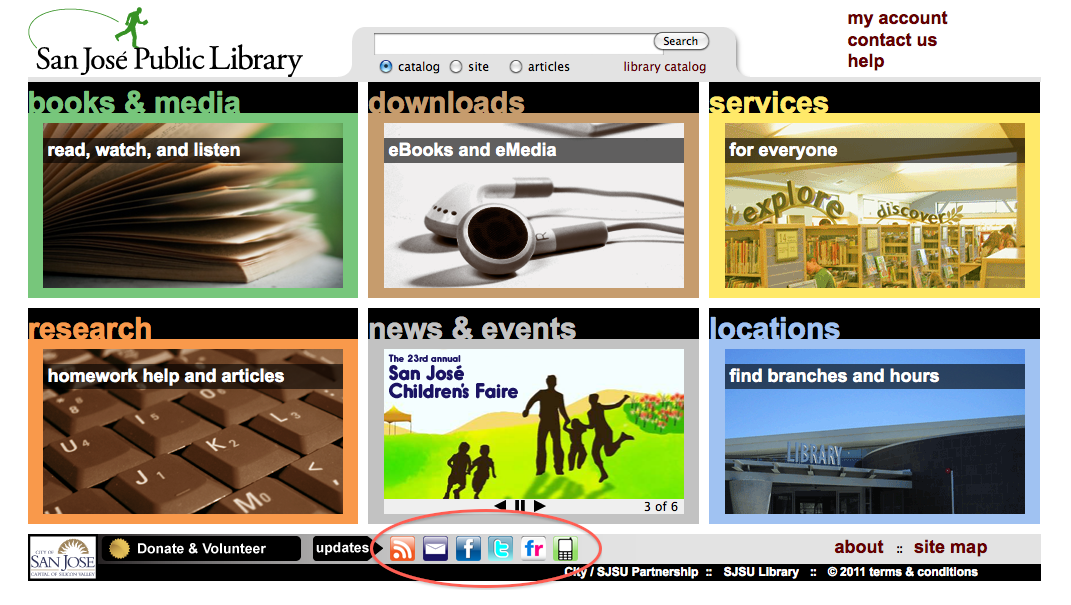
Let’s take a comparative look at a few libraries that feature Web 2.0 services: the San Francisco Public Library, the San Jose Public Library, and the Los Angeles Public Library. Here are some screen shots of their homepages:
Access points to mobile services and e-Media, such as LAPL podcasts and vodcasts. It’s interesting to note that social media applications are not accessible anywhere on the main page.
All Web 2.0 applications are accessible from the icons at the bottom of the page. Out of the three public libraries, this interface features the best and most straight forward access points.
Here is a comparative breakdown of the different services that each public library offers:
| San Francisco Public Library | Los Angeles Public Library | San Jose Public Library |
| RSS feeds | RSS feeds | RSS feeds |
| IM service | IM service | IM service |
| Mobile interface | Mobile search application | Mobile search application |
| Podcasts | Podcasts | Podcasts |
| Vodcasts | Vodcasts | Vodcasts |
| Blogs | Blogs | |
| Delicious | Flickr | |
| LibraryThing | ||
| GoodReads |
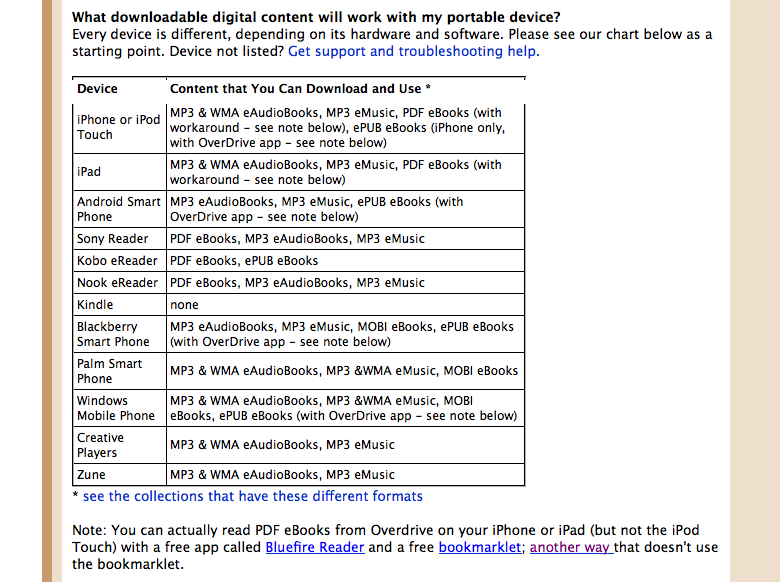
Couple of contrasting points worth mentioning. One point is the surprising lack of social media software utilized at the Los Angeles Public Library. Out of all Web 2.0 features offered, the mobile search application was the most prominent and easiest to find, with podcasts and vodcasts following second. RSS feeds could only be found after a thorough website search. The San Jose Public Library on the other hand had RSS feeds for practically everything, and nearly all Web 2.0 services are accessible from the Get Updates page. Additionally, between the three library sites, the San Francisco Public Library utilized more social bookmarking tools geared for reader advisory services. A last point of interest, is the technology service focus of the San Jose Public Library, exemplified by the device format listing on the FAQs About Digital Content page:
Let’s take a closer look at podcasts and vodcasts, since all three libraries utilizes these services. The SFPL offers very limited podcasting in comparison to the SJPL and the LAPL. SFPL podcasting spans from 2007-2009, featuring local readings, spoken word, discussions, and performances. SJPL podcasts span from 2010-2011 and are mainly composed of poetry readings and staff pick recommendations. The LAPL features three different podcast programs, Children’s podcasts from 2008-2009, interviews and talks on Richard Neutra the architect, and the ALOUD at Central Library speaker series. The ALOUD series has been a part of the LAPL since 1993 and features “leading figures in the worlds of literature, the arts and ideas. These dynamic programs are designed to contribute to an informed, engaged, and democratic community and to foster life-long learning in a welcoming environment. The great majority of ALOUD programs are presented free of charge to the people of Los Angeles” (from ALOUD at Fora.tv). Between the three libraries, the LAPL offers a strong variety of podcast topics, spanning over a 10+ year period. The utilization of vodcasts also offer an interesting comparison. The SFPL, again seems to offer surprisingly little in terms of diverse topics and readings. SJPL, on the other hand, has a wide variety of vodcasts centered on community events, story times, staff picks, library tours, and overall community participation all featured on the library’s blip.tv channel. Again, the LAPL’s vodcasting exclusively features ALOUD talks, lectures, and discussions.
The use of podcasting and vodcasting offers an interesting snapshot of how each library frames their services. The lack of user-centered social media services at the LAPL and the overall top-down podcast and vodcast programing, frames the LAPL as a kind of cultural mecca. The SJPL on the other hand, utilizes vodcasting as an archival and broadcasting tool for community events and participation, offering a very clear picture of the kind of communities these libraries serve. The SFPL seems to be situated somewhere in-between, offering some forms of top-down programming but with some awareness of the importance of having some user-centered services, albeit with inconsistent application. However, it is important to keep in mind that these differences may have more to do with funding and budgetary constraints, rather than mere variations in community or user orientation.
Between these three libraries, I would probably be more inclined to use the SJPL vodcasting services if I were a new local patron wanting to get a sense of my local community, and the LAPL podcasting and vodcasting for cultural enrichment. For SFPL, I might be inclined to utilize their social media applications for reader advisory purposes, but I would be less drawn to their limited podcast and vodcast programming. I do think that the SFPL and LAPL could learn from SJPL website interface, user-centered focus, and overall usability regarding Web 2.0 applications and I think that the SFPL would benefit from re-evaluating their social media strategies, goals and purposes in support of local communities, local writers and authors, or local issues within California generally.
…and on that note, I’d like to end with a reference to a SFPL video talk with Stacy Alderich, California’s State Librarian, and her discussion of the California budget crisis and where libraries are heading. What I find particularly interesting is her focus on technology trends rather than on the overall statewide trend of slashing funding for public services and the plateaued unemployment rate. Again, it does seem as though California has been facing larger structural issues that go beyond the question of “How can we offer the same level of services for less?”
OK, I’m off of my soap box.
Trackbacks