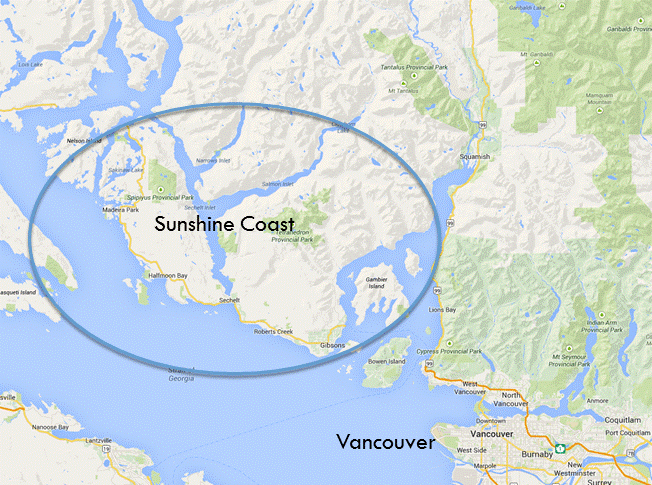
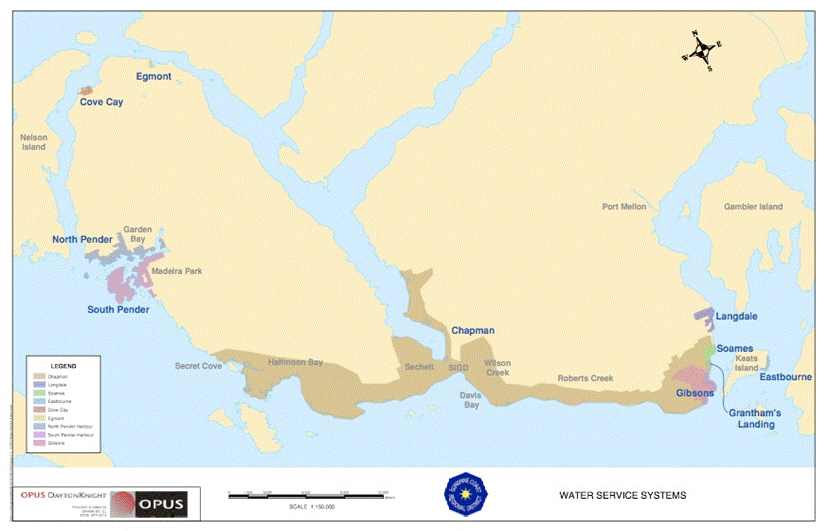
The Sunshine Coast consists of numerous small coastal communities that lie within the South Coast of British Columbia and is located approximately 50 km northwest of Vancouver (Figure 1). The Sunshine Coast spans from Earls Cove to Langdale and has a total population of approximately 28,070 (Statistics Canada, 2013). Within this area, approximately 90% of the residents live within the Regional Water Service Area (RSWA), which spans from Secret Cove to Langdale and includes multiple water systems (Figure 2). The Chapman water system, which is the focus of this study, is the largest water system within the RWSA. The Chapman water system supplies approximately 90% of the population within this water service area and in 2013, the service population was estimated to be 22,000 (SCRD, 2013).
Figure 1: Map of the Sunshine Coast, BC (depicted in blue shaded area) in relation to Vancouver, BC (maps.google.ca)
Figure 2: Map of all of the water systems on the Sunshine Coast, BC, and the approximate locations of the three climate stations (orange stars), with station ID in brackets, used to collect climate data as discussed in the Data Collection Section (Climate) of this report. The Chapman water system is depicted in the brown shaded area (SCRD, 2013)
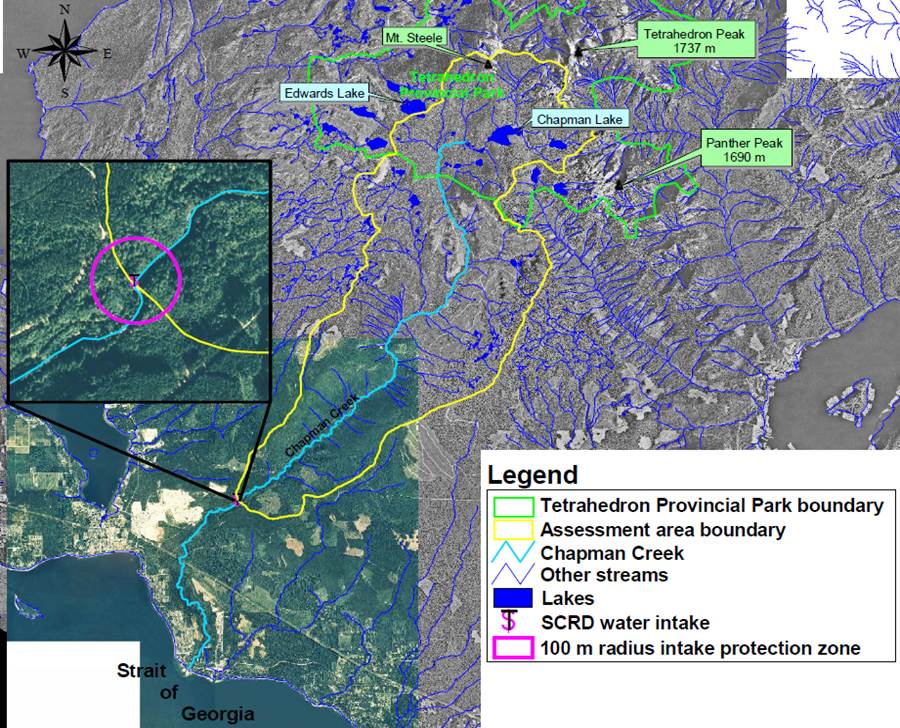
The Chapman Creek watershed is the primary water source for the Chapman water system and consists of a watershed area that is approximately 73 km2 (SCRD, 2006) (Figure 3). Within the Chapman Creek watershed there are three biogeoclimatic zones: Coastal Western Hemlock (CWH), Mountain Hemlock (MH), and alpine. About 25% of the catchment is above 850 m, which is the current elevation where snow pack starts to hold significant snow water equivalent (Beaulieu et. al., 2012). Chapman Creek maintains a hybrid streamflow regime characterized by a winter freshet influenced by heavy precipitation in November and December and a spring freshet influenced from snowmelt in April, May and June (Carson, 1998).
Chapman Lake is the primary water storage reservoir for the Chapman water system and water from the lake is released into the creek through an impoundment structure during the summer season (typically July to September). For the rest of the year, water flows over the impoundment structure and into the creek under natural conditions. Edwards Lake is the backup storage reservoir and total lake storage between the two lakes is approximately 1.8 million m3 of water. Water from Chapman Creek is diverted into an intake for the water treatment plant (WTP), which is operated by the Sunshine Coast Regional District (SCRD).
Figure 3: Delineation of the Chapman Creek drinking water watershed and the intake to the water treatment plant that supplies water to the Chapman Creek water system for area residents on the Sunshine Coast near Sechelt, BC (SCRD, 2006)