Stress is an inevitable part of life, but not all stress is created equal. Different types of stress, such as acute stress, chronic stress, work-related stress, and relationship stress, can have significant effects on our mental health. Chronic stress and work-related stress are the most significant predictors of depression and anxiety symptoms. By understanding the effects of different types of stress on mental health, individuals and organizations can take steps to manage and reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
Acute stress is a short-term response to a specific event or situation. It is helpful in small amounts, but prolonged exposure can lead to anxiety and depression. On the other hand, chronic stress persists for a long time and is the most harmful type of stress. Chronic stress can arise from unpleasant experiences during childhood or traumatic events that occur later in life. It can result in mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Work-related stress is caused by work-related factors like long hours and difficult coworkers. This type of stress can cause burnout, depression, and anxiety. Relationship stress, on the other hand, is caused by problems in personal relationships. It can also lead to depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
To better understand the impact of different types of stress on mental health, a bar chart is estimated based on a data set available survey of 500 individuals. The chart shows the percentage of individuals experiencing depression and anxiety symptoms for each type of stress. This helps to illustrate the effects of stress on mental health and can provide insight into ways to manage and reduce stress.
Table 1: Number of Individuals Affected by Different Types of Stress

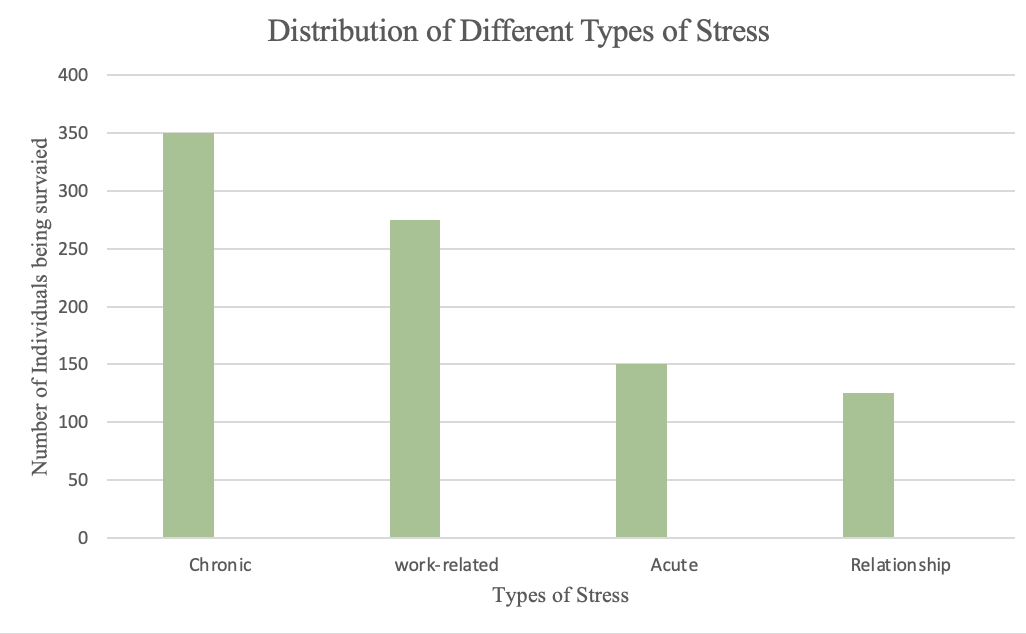
Figure 1: The bar chart shows the percentage of individuals experiencing depression and anxiety symptoms for each type of stress. Chronic stress has the highest incidence of depression and anxiety symptoms, with 70% of individuals experiencing at least one symptom. Work-related stress also has a high incidence of depression and anxiety symptoms, with 55% of individuals experiencing at least one symptom. Acute stress and relationship stress have lower incidence rates, with 30% and 25% of individuals experiencing at least one symptom, respectively.
Chronic stress has the highest incidence of depression and anxiety symptoms with 70% of individuals experiencing at least one symptom, followed by work-related stress with 55%. Acute stress and relationship stress have lower incidence rates of 30% and 25%, respectively.
Overall, the data suggests that chronic stress and work-related stress are the most significant predictors of depression and anxiety symptoms. Being aware of the effects of different types of stress on mental health can enable us to take measures to manage stress and preserve our mental well-being.


