Have you ever come across someone in your life, who hated music? Did you force them to listen to your favorite song and expected them to get excited but you got a poker face instead? Did you fully give up and just assumed that they were a weirdo? Well to be honest they aren’t weird, its just that they are unique in their own way! And most likely they might be experiencing a condition called as Specific Musical Anhedonia!

Source: Neurocurean.com
Anhedonia is a condition wherein a person is unable to derive pleasure from any activity, in simpler terms it could also be referred to as depression. Musical anhedonia is a specific form of anhedonia, wherein a person is able to experience pleasure in every other activity however when it came to music, they couldn’t care less!
Although it is not a serious medical condition, did you know this condition is experienced by 3-5% of the global population? Well you could say that’s a small percentage of people, but why should you care? Read more to find out!
According to a recent study published in the journal of PNAS, researchers were able to establish the neurological basis of this condition. The study provides a direct evidence that sensing pleasure from music is mostly likely linked to the reward processing center of the brain. Well what exactly does this reward processing center do? Let me break it down in simpler terms, did you ever win money while gambling, had the first sip of hot chocolate you were craving for the entire day! what was the first thing you felt after doing these above activities, you must have gained some sense of pleasure right!. So,the reward processing center in the brain mostly helps in experiencing pleasure from most activities like good food, monetary gains, sex etc..
Based on the observations conducted on people with different spectrums of interest towards music, the researchers through brain imaging analysis (fMRI) were able to decipher that music anhedonia is most likely caused due to less connectivity or wiring between the auditory cortex (associated with hearing) and the reward processing center in the brain.
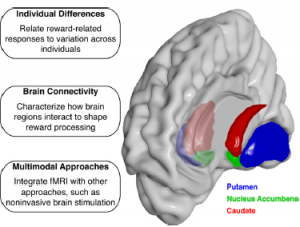
Source: S.K Wang et al (2016) American journal in Physiology
What do you think would be the significance of the study? The findings of the study conducted could potentially be used to develop new reward based therapies for people experiencing depression, autism and gain further insight about other addiction based disorders. This could probably help us understand reward mechanisms in connection with different regions of the brain. Also, one could probably be able to look into the evolutionary aspect of how music integrated itself as a pleasurable activity in the lives of us humans!

Source: Billboard.com
So now that I provided you with some extremely rewarding information , I hope you are amazed with how differently each of our brains are wired and how different each of them function and help us experience things!
Fun fact: One ongoing research on music anhedonia is actually funded by the Grammy museum!
Published on 18th November 2019
-Harshitha Nagesh