Q: What’s the big problem here with Salmonella?
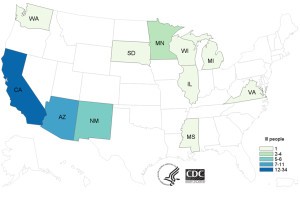
A: A Salmonella seafood outbreak that hit United States has caused 62 sick across 11 states as of July 20, 2015. US CDC reported that there were 11 cases of hospitalization and no case of deaths. 97% of the infected population recalled the consumption of sushi with raw tuna a week before becoming ill. Results from laboratory and epidemiological investigations indicated that these people were likely infected with Salmonella Paratyphi B variant L(+) tartrate(+). Raw tuna processed in Indonesia by Osamu Corporation were confirmed responsible for 18 cases in California and some cases of infections in Minnesota.
As a result, on July 21, 2015 Osamu Corporation called for a voluntary recall of two categories of items, frozen tuna and yellowfin tuna, processed in their Indonesian plant.
Q: Isn’t Salmonella usually found in eggs and poultry?
A: As known to the general population, Salmonella is often associated with foodborne illness due to its growth in poultry and egg products, as well as produce and complex foods. An interesting fact is that Salmonella is also a common pathogen found in seafood. Together with Shigella, these two pathogens constitute up to 10% of the reported foodborne illnesses in United States. Fish, shrimp, oysters and clam are food vehicles most often associated with seafood outbreaks.
Want to know more? Here is a relevant video about Salmonella in seafood (published 3 years ago):
Q: “Who” is Salmonella? Where is it from? How is it identified?
A: Salmonella is a gram negative, rod shape, facultative anaerobic, non lactose fermenting bacillus with as much as 2500 serotypes identified. Transmission routes can include food-borne and water-borne, person to person and contact with animals. According to US FDA, Salmonella can be found in seafood that is intended for minimal processing and cooking.
The source of this contamination can be traced back to the acquisition of the bacteria in polluted waters. Therefore to prevent outbreaks, current measures are carried out in harvesting waters before the final harvest. Another route of contamination can be traced to the processing and storage of the seafood.
Laboratory test of stool samples from infected patients are used for diagnosis of salmonellosis. Further tests are required to discover the subtype of Salmonella responsible for the illness.
Q: Yikes! What are the symptoms of salmonellosis?
A: Salmonellosis, an infection caused by Salmonella, can cause acute gastroenteritis, accompanied by symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps from 6 to 72 hours. Headaches, nausea and vomiting in individuals may also be visible. However these symptoms usually disappear in 4 to 7 days, when many people recover. During this period, large volume of liquid is required to replace lost fluid from diarrhea. Severe manifestations include enteric fever, urinary tract infections, bacteremia and severe focal infections. Up to 10% of patients with typhoid fever can develop serious complications.
In the circumstance of bacteremia, Salmonella can spread from intestines to blood eventually causing severe illnesses leading to death. Antibiotics may be applied to cure the disease, however antibiotic resistance is a perplex issue. Chronic pain in joints, urination pain and irritation of eyes can be some long term complications. In severe cases, chronic arthritis is observed in these patients.
Q: Who is more likely to be infected? Are there any patterns that can be observed?
A: Within the infected population, pregnant women, immuno-compromised individuals, young children (<5) and seniors (>65) are most likely at risk for developing severe disease. Consequently these individuals are advised to avoid consumption of raw finfish and shellfish. Patterns have been recorded regarding age and season: infants and elderly are on top of the list for being most vulnerable to salmonellosis; those infected individuals who consume contaminated food during the summer and early fall seasons are likely to contribute to the infection numbers.
Q: What about… specifically Salmonella Paratyphi B variant L(+) tartrate(+)?
A: Salmonella Paratyphi B variant L(+) tartrate(+) (formerly Salmonella Java) belongs to the subspecies of Salmonella enterica and is known to cause non-typhoid salmonellosis. In contrast, Salmonella Paratyphi B variant L(+) tartrate(-) causes paratyphoid fever.
Q: How should we “wrestle” with the pathogen especially in seafood?
A: Besides usual ways of avoiding foodborne illnesses, effective methods of preventing foodborne illness in specifically seafood, as suggested by US FDA, include:
- Washing hands, utensils and cooking surfaces
- Cooking seafood for 15 seconds at minimum of 145oF
- Avoid cross contamination by separating raw and cooked seafood
- Storing seafood below 40oF in the refrigerator or below 0oF in the freezer
And finally… Questions for you!
- What is a possible reason for Salmonella to be able to grow in frozen raw tuna?
- What are some possibilities that the infection cases can occur over 11 states (possible routes)?
Salmonella in raw tuna articles:
http://bigmedicine.ca/wordpress/tag/salmonella-paratyphi-b-variant-l-tartrate/#sthash.VN7LcdMj.dpbs
FYI… Check it out! (References:)
Epidemiology of Seafood-associated infections in United States:
http://cmr.asm.org/content/23/2/399.full
Facts on Seafood safety:
http://seafoodhealthfacts.org/seafood_safety/practitioners/microbes.php
Salmonella Q&A:
WHO document on Typhoid Fever:
http://www.who.int/rpc/TFGuideWHO.pdf
WHO document on Non-typhoid fever:
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs139/en/
Government of Canada guidelines:
Paratyphoid fever:
http://www.health.alberta.ca/documents/Guidelines-Paratyphoid-Fever-2014.pdf
Youtube video on this case:


14 responses to “Salmonella: in Frozen Raw Tuna?”