Rishabh Kapoor | MEL Candidate | Dec 14, 2023 | Room C400 | 10:30 – 11:00
Mentor: Airton Dudzevich, BC Hydro
ABSTRACT
To achieve Net Zero Emissions by 2050, the scenario envisions a massive deployment of variable renewable sources of power such as solar, hydro, wind power, and bioenergy, along with an increase in overall electricity demand as more end users electrify. The implementation of grid-scale storage, notably batteries, pumped hydro, and hydrogen, will be essential to manage the impact on the power grid and handle the hourly and seasonal variations in renewable electricity output while maintaining grid stability and reliability.
A pumped-storage hydropower system is the most widely used technology for storing energy, and it has considerable additional potential in several regions. In recent years, the battery market has experienced strong growth, making it the most scalable type of grid-scale storage. Furthermore, hydrogen is an emerging technology that offers the potential for the seasonal storage of renewable energy.
INTRODUCTION
As of 2021, Canada boasts a total installed capacity of 150 GW, yet its energy storage capacity remains underwhelming at less than 1 GW. Despite the multifaceted benefits offered by energy storage technologies, Canada has yet to fully harness them, with only a limited utilization of these services. Key stakeholders must enhance their comprehension of energy storage and become more acquainted with its diverse applications. The existing market structures and valuation methods fall short in providing investors with lucrative revenue opportunities, making it challenging to justify the substantial investments required. Remarkably, Canada’s transmission and distribution lines are underutilized, operating at a fraction of their capacity on average. The viable solution lies in leveraging energy storage as a grid optimization technology, offering not only low-carbon grid flexibility but also cost reductions for consumers. This strategic approach addresses the current limitations and unlocks the potential for a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape in Canada.
This project aims to tackle the escalating energy storage requirements of utility power companies within the evolving energy landscape. Its primary goal is to investigate large-scale energy storage solutions that can enhance the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of power generation and distribution. The growing appeal of energy storage is attributed, in part, to its increasing affordability. Notably, the cost of lithium-ion batteries, a highly effective technology for energy storage, has seen a remarkable 90% reduction over the past decade, as indicated by Bloomberg NEF, with an additional 6% decrease in the past year. As the costs of various storage technologies continue to diminish, we are approaching a point where we can more accurately assess the potential of energy storage in supporting Canada’s transition toward a fully decarbonized and expanded grid. A Comparative Techno-economic analysis has been executed, evaluating different power capacities and timeframes, and comparing the three most promising energy storage technologies—Pumped Hydro, Battery Energy, and Hydrogen—in the Canadian context.
METHODOLOGY
The methodology entails a comprehensive exploration of energy storage solutions tailored for power utility companies in Canada, with a specific focus on the province of British Columbia (BC). The initial phase involved compiling an extensive inventory of diverse energy storage technologies, incorporating their respective efficiencies, costs, and scalability factors. To ensure the robustness of the data, a combination of research studies, industry reports, real-world data, and government publications was systematically analyzed. The technical analysis then delved into the specific requirements and suitability of these energy storage solutions for the Canadian and BC contexts. Subsequently, the economic viability of large-scale energy storage solutions for utility companies was rigorously assessed, considering factors such as cost-effectiveness, long-term sustainability, and potential economic benefits.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
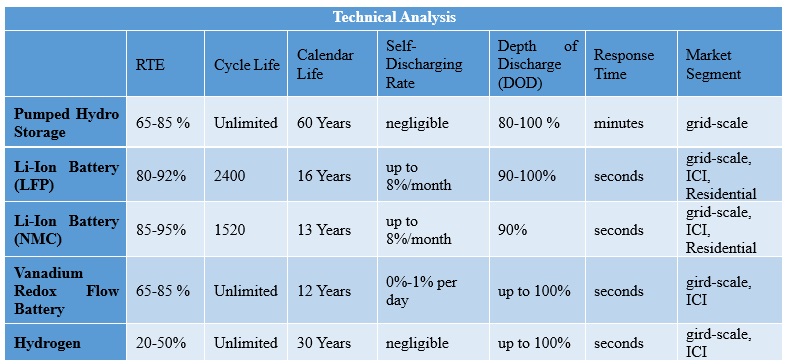
Various energy storage technologies exhibit distinct characteristics. Pumped Hydro Storage is ideal for grid-scale applications, boasting 65-85% RTE and a 60-year Calendar Life. Li-Ion Batteries (LFP and NMC) cater to grid-scale, industrial, and residential needs, offering high RTE (80-95%) and diverse Cycle and Calendar Life spans. Vanadium Redox Flow Battery suits grid-scale and industrial use with variable RTE (65-85%) and a 12-year Calendar Life. Hydrogen is suitable for grid-scale and industrial sectors, featuring an RTE of 20-50% and a 30-year Calendar Life. Differences exist in self-discharging rates, depth of discharge capabilities, response times, and targeted market segments.
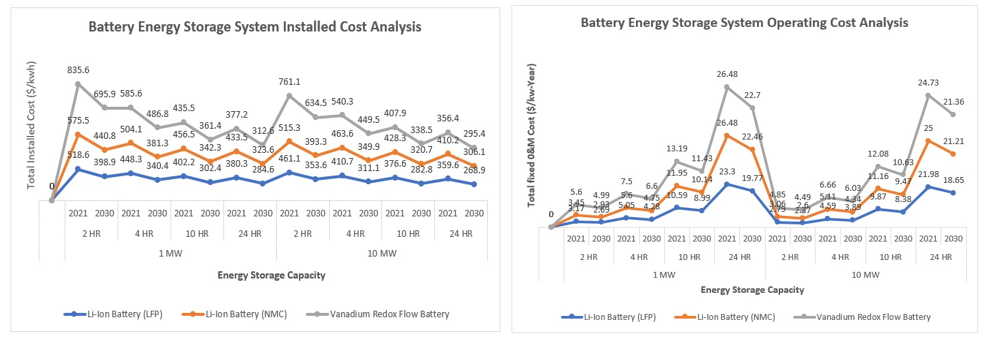
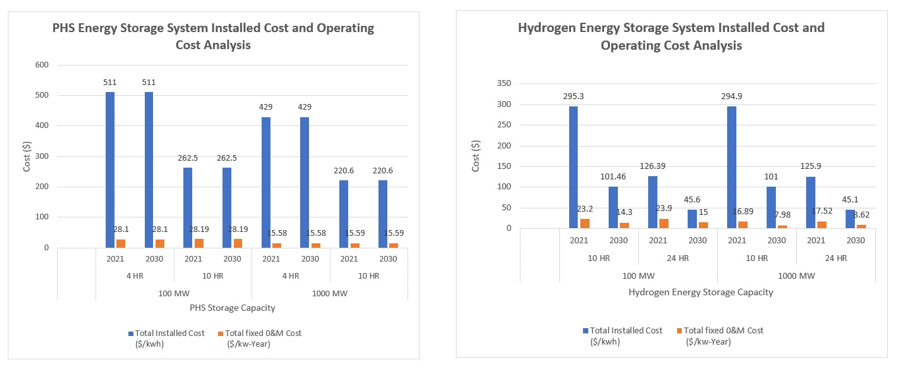
The results of the energy storage technology comparison reveal significant trends in Total Installed Cost ($/kWh) and Total Fixed O&M Cost ($/kW-Year) across different capacities and durations. Li-Ion Battery (LFP) shows a consistent decreasing cost trend from 2021 to 2030, making it an economically attractive option for various applications. Li-Ion Battery (NMC) and Vanadium Redox Flow Battery also follow a similar decreasing cost pattern, enhancing their competitiveness. Pumped Hydro Storage maintains a stable cost over the studied period. Hydrogen storage systems, despite their low round-trip efficiency and high operating costs, display a notable cost reduction for the 10 HR and 24 HR durations, positioning them as potentially competitive options in the future market. In terms of Total Fixed O&M Cost, Li-Ion Battery (LFP) and (NMC) demonstrate decreasing trends over time, making them appealing for both small and largescale applications. Vanadium Redox Flow Battery maintains a consistent pattern, while Pumped Hydro Storage exhibits the same O&M costs for the 100 MW and 1000 MW capacities in 2030. Hydrogen storage systems exhibit a substantial reduction in O&M costs, particularly for the 10 HR and 24 HR durations, indicating their potential competitiveness in the market. kW-year
CONCLUSION
The results and trends in techno-economic analysis provide a crucial guide for power utility companies in making informed decisions regarding the adoption of energy storage solutions aligned with their operational needs and economic considerations. The comparison underscores the diverse opportunities and challenges associated with each energy storage technology. Pumped Hydro stands out for its mature technology, low energy costs, and long lifetime, but faces hurdles in geographical constraints and high initial investments. Li-Ion Battery (LFP) and (NMC) offer high efficiency, with decreasing costs over time, but present challenges related to lifetime cycling and safety. Vanadium Redox Flow Battery provides a long cycling lifetime but with limitations in energy and power density. Hydrogen Storage offers long-duration storage, but its low round-trip efficiency and high operating costs pose challenges. Each technology serves specific purposes, and the selection should be based on a careful evaluation of trade-offs between opportunities and challenges, as well as the specific services required.
REFERENCES
- Priorities for supporting the decarbonization of Canada’s grid with energy storage. (n.d.). https://renewablesassociation.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/CanREA-EnergyStorage-Jan2022-Eng.pdf
- DOE Global Energy Storage Database. (n.d.). Sandia.gov. https://sandia.gov/ess-ssl/gesdb/public/projects.html
- A study on the energy storage market in Canada Final report prepared for Natural Resources Canada. (n.d.). https://www.naviusresearch.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/2021-03-Energy-storage-market-in-Canada.pdf
- 2022 Grid Energy Storage Technology Cost and Performance Assessment. (n.d.). Energy.gov. https://www.energy.gov/eere/analysis/2022-grid-energy-storage-technology-cost-and-performance-assessment