Nurlan Smailov | MEL Candidate | Dec 14, 2023.
Mentor: Charles Borromeo, Solaris Management Consultants Inc.
ABSTRACT
Ammonia is pivotal in sustaining the global food chain and advancing clean fuel technologies. With its nitrogen-rich composition, ammonia is a crucial component in fertilizers, contributing to 80% of its industrial-scale utilization and 50% of the world’s food supply. Furthermore, its high hydrogen content positions ammonia as a promising clean combustion fuel, aiming to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. With a volumetric energy density three times higher than compressed hydrogen and approximately ten times greater than lithium-based batteries, ammonia emerges as a leading candidate for storing, transporting, and delivering clean energy.
The development of green ammonia production has been targeted as a low-carbon alternative to conventional, emission-intensive methods. Achieving emission-free and cost-effective ammonia production is a significant focus, necessitating an understanding of critical parameters for optimization. The study underscores the considerable potential for West Canada to supply clean fuel to the Asian and North American markets, specifically by investigating the feasibility of establishing a cost-competitive green ammonia production in British Columbia, Canada (B.C.).
INTRODUCTION
Canada’s economy relies on materials produced by the chemical and fertilizer industry. The sector’s emissions account for the same amount as the steel and cement sectors combined.
Historically, Canada had experience producing ammonia through hydropower, but facilities were decommissioned since they were not cost-competitive against ammonia from natural gas.
Anticipating substantial growth in these markets in the coming years, driven by escalating efforts toward decarbonization, energy independence, and supply diversification, Canada reevaluates its potential in clean ammonia. There are several renewable hydrogen and ammonia projects in progress in Eastern Canada.
This study explicitly targets B.C., examining the province’s potential in light of available clean hydropower resources and strategic logistical access to Asian and North American chemical and energy markets.
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the economic feasibility of emission-free ammonia production in British Columbia, Canada.
METHODOLOGY
The economic dimensions associated with the large-scale production of ammonia through water electrolysis in combination with Haber Bosch ammonia synthesis using grid hydropower have been investigated. The approach involved utilizing a chemical process simulation model in tandem with a levelized cost of production estimator tool to gauge the sensitivity of levelized costs of ammonia to critical parameters, including facility scale, equipment, and grid electricity costs.
The production cost of emission-free ammonia has been compared to market sales prices and fossil ammonia cost, factoring in carbon pricing relying on the literature forecasts.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The primary determinant influencing ammonia production through electrical power (Power to Ammonia) was the energy cost. Up to 40-50% of the ammonia cost can be attributed to the electricity cost. The best-case scenarios anticipate that green ammonia can be cost-competitive with fossil ammonia by 2030.
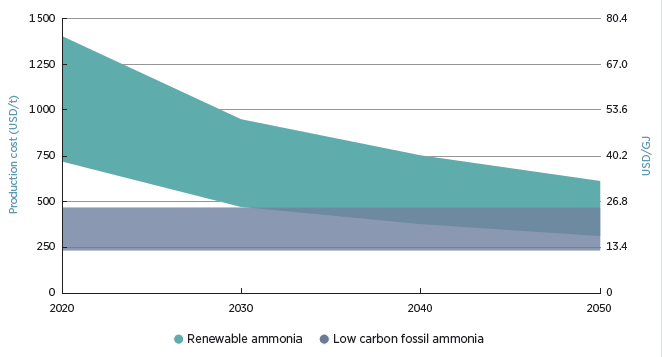
Figure 1 Current and future production costs of Renewable and Low carbon ammonia, IRENA (2022).
The current cost of electricity in B.C., as per the Clean Industry and Innovation Rate, is 40-50 CAD/MWh. Meanwhile, the 20 CAD/MWh is estimated to lower the production cost to the higher cost range of the low-carbon ammonia. Concerning greenhouse gas emissions, the B.C. grid yields 0.23 kg of CO2 equivalent per kilogram of ammonia (NH3) in a fully grid-connected facility and meets the criteria outlined in the Green Hydrogen Standard.
Regarding revenue streams, ammonia sales to domestic and international markets are more economical than energy storage applications.
On the global stage, China is anticipated to actively transition to green ammonia as a substitute for its expensive coal-based ammonia.
Within the domestic market, the eastern provinces of Canada hold a competitive advantage due to lower hydroelectricity costs and a deregulated power market.
In addition to European and Asian markets, the U.S. should be targeted as an major importer of Canadian clean ammonia.
REFERENCES
1. Nguyen, T., Abdin, Z., Holm, T., Mérida, W. (2019). Grid-connected hydrogen production via large-scale water electrolysis. Energy Conversion and Management, 200, 112108. ISSN 0196-8904.
2. Shepherd, J., Khan, M. H. A., Amal, R., Daiyan, R., MacGill, I. (2022). Open-source project feasibility tools for supporting the development of the green ammonia value chain. Energy Conversion and Management, 274, 116413. ISSN 0196-8904.
3. International Renewable Energy Agency. (May 2022). Innovation Outlook Renewable Ammonia.