Like many students at UBC, I rely on coffee to get me going throughout the day. I always have a tall americano from Starbucks in the morning and lately I’ve been getting a second cup in the afternoon as well. It’s come to the point where I’ve been told that I need to cut back and reduce my daily caffeine intake. But recent studies have shown that it may not be so bad for you after all.

Coffee. Image source: My Mzone
For example, did you know a cup of coffee has up to four times more antioxidants than green tea? In fact, scientists have discovered that it can contain more antioxidants than a typical serving of fruit, such as: blueberries, raspberries, and oranges. However, new research has shown the effectiveness of antioxidants may be lessened for those who add milk or cream to their coffee. This is due to the fact that when milk or cream is added, it binds to the antioxidants and therefore lessens its effectiveness.
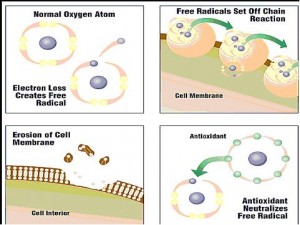
Effect of Antioxidants. Image source: Lean it up
Antioxidants are very important for us because they help fight oxidation. This is a chemical process that occurs naturally in our body every day. When this natural process is disrupted, free radicals are created. These are highly unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells in the body if left uncontrolled.
Also, researchers have found that coffee can reduce the risk of stroke. A study at the Harvard School of Public Health followed a group of women over a 24-year period. The group consisted of 83, 076 women who participated in the Nurses Health Study that had no history of stroke, coronary heart disease, diabetes, or cancer. Their coffee consumption and amount of strokes were recorded from 1980 to 2004. They were able to conclude that those who drank coffee reduced their risk of stroke by 20%.
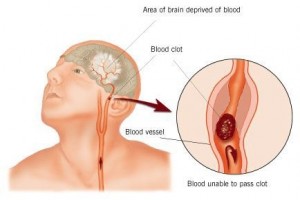
Cause of Stroke. Image source: Flickr
In addition, a study in Finland suggests that coffee offers protection against Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The researchers randomly selected 1409 participants and followed them over a 21-year period. They were specifically focused on the coffee consumption of participants at midlife and the occurrence of being diagnosed with Alzheimer’s or dementia later on in life. Surprisingly, a 65% decrease in disease was found in people who consumed coffee daily.
So next time you think about kicking your coffee habit to the curb, remember all of these health benefits it’s linked to.

Coffee Beans. Image source: Wikimedia Commons
Below is a video that describes in more detail the effects of antioxidants and caffeine in coffee.
References:
-http://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2011/10/antioxidants-explained-why-these-compounds-are-so-important/247311/
-http://www.naturalnews.com/025737_coffee_risk_drinking.html
-Angelica Reyes