In cities such as our own, gluten-free products are becoming increasingly available throughout grocery stores and restaurants. With exception of the health-conscious members of society, who is the primary consumer of these products? One such group is the portion of the population affected by the disorder known as celiac disease.
Rather eating gluten-free for health benefits, celiacs depend on these foods daily to avoid painful illness. In the United States, researchers estimated a prevalence of 1 in 141 peoples affected by celiac disease. Among the people affected many had been undiagnosed leading the researchers to conclude that celiac disease is not as rare as believed in previous years.
What is celiac disease?
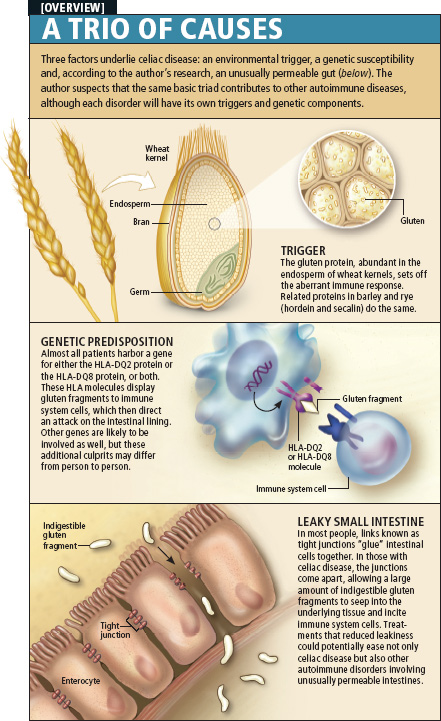
What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a disorder that inhibits those affected from consuming foods with gluten-containing ingredients such as wheat, barley, and rye. Celiac disease harms the small intestine making it incapable of absorbing nutrients during the digestion process which leads to illness. Celiac disease means an abnormal self-defence response is triggered within the body when gluten is consumed causing damage to the small intestine. If celiac disease is left undetected or untreated, common adverse health effects associated include anaemia (iron deficiency caused by iron loss) and osteoporosis (reduced density of bone material that increases chance of fracture). For example, anaemia as an adverse health effect from celiac disease can result because anaemia can be caused by a Vitamin B12 and iron deficiency. Because Vitamin B12 and iron are absorbed in the small intestine, this poses a problem for celiacs whose small intestines are damaged, leading to anaemia that will cause fatigue, weakness, and additional categorical anaemic symptoms.
Figure 1. Image outlining the causes of celiac disease. Source: Kim Moss Electronic Publishing Services Inc.
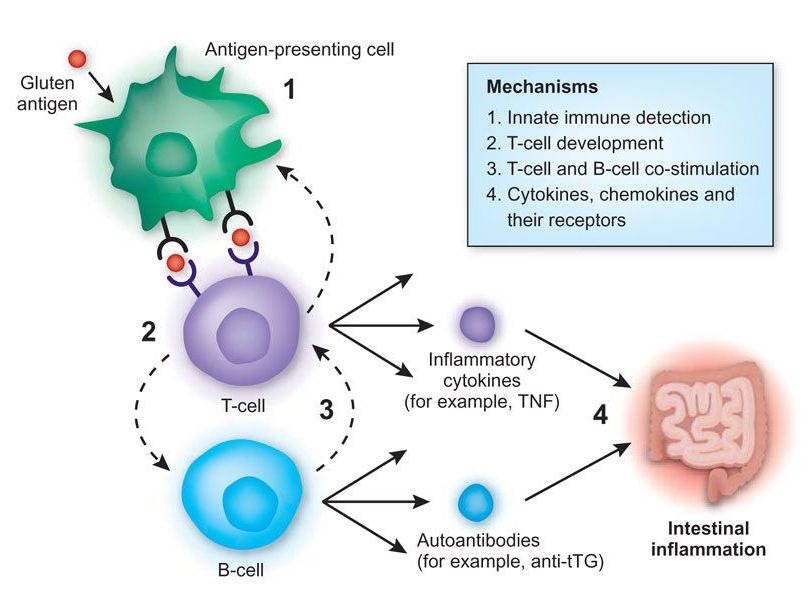
Figure 2. Simplified diagram outlining the pathway of inflammation (swelling) for celiac disease caused by gluten antigens (foreign substance that induces a reaction). Source: Nature Genetics
https://youtu.be/nXzBApAx5lY
Video: Celiac disease – causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and pathology. Osmosis YouTube channel.
Why is gluten triggering this disease and how is this discovery a leap forward for the celiac community?
Why is gluten causing these symptoms in people around North America? Gluten is composed of proteins called prolamins that are storage proteins (store key survival components for cells such as amino acids or metals). Prolamins are found in wheat, rye, barley, and corn which are common food ingredients. In a recent study conducted in Austria, a research team has discovered a method that provides the possibility of future treatments for celiac patients. The researchers utilized antibodies (proteins that neutralize invaders such as bacteria) to create fragments that bind and neutralize prolamins. Celiac disease currently requires a gluten-free diet that is expectedly followed religiously. The fragments created bind grains containing prolamin in everyday ingredients and has provided future studies the potential to revolutionize clinical treatments that improve quality of life. Discovered treatments can eventually be used to mask the prolamin, preventing it from being displayed to immune cells so an autoimmune response (self-immune response) is not triggered.
Before believing that you are affected by celiac disease, please be aware that irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and intolerances to foods such as dairy are similar in symptoms. No need to panic yet, but always be sure to check with a physician if you are experiencing symptoms! With the prevalence of celiac disease in the United States being 1 in 141 people, a treatment to reduce gluten sensitivity or inhibit it completely would improve many lives. The production of the antibody fragment that targets prolamin is a leap for the celiac community.
– Vanessa Niedzielski

One response to “One small fragment to bind a protein, one leap for celiacs!”