Rural communities in developing countries across the world face this problem in a way developed nations are lucky to not experience. When driving down the highway, you may notice larger vehicles running on gases such as diesel spewing clouds of black smoke. Additionally, in industrial-based cities such as Edmonton, factories can be seen from each direction bellowing black smoke into the air. What is this black smoke and why do we care?
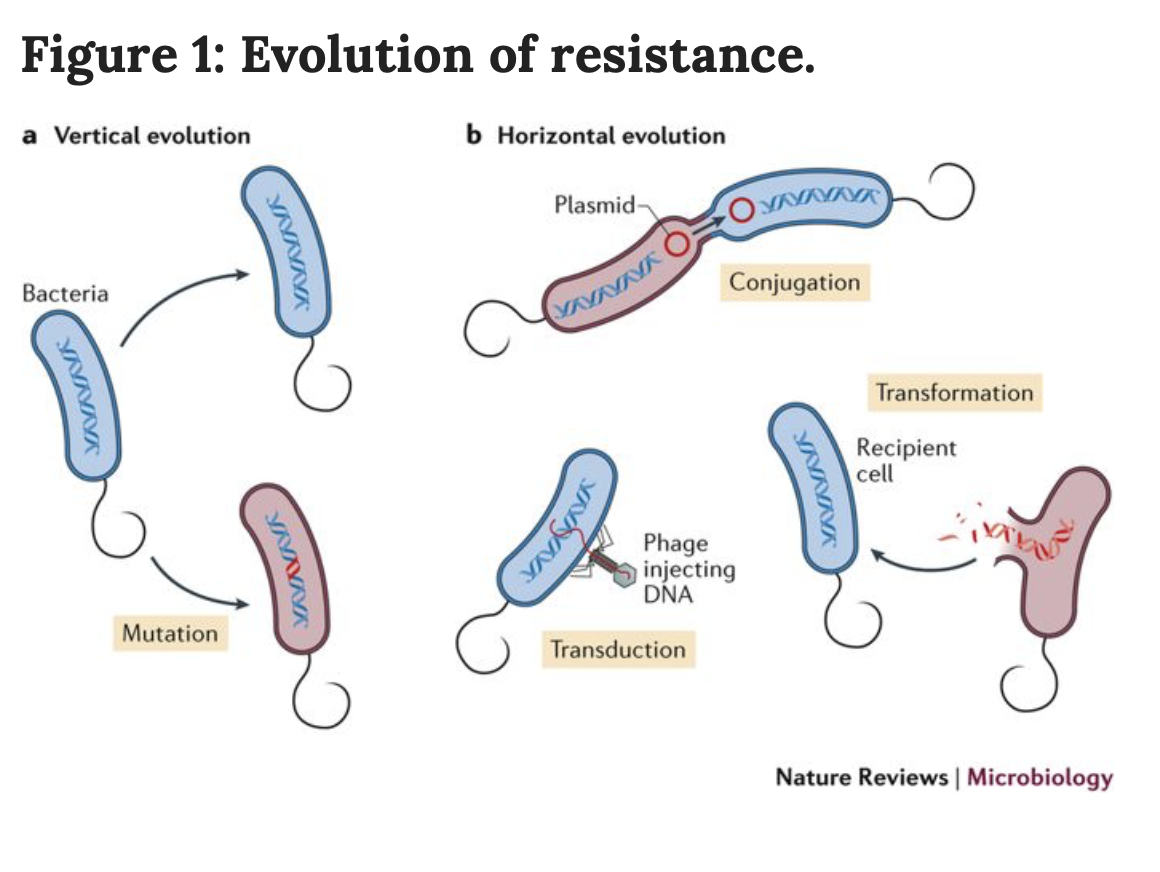
Black Carbon
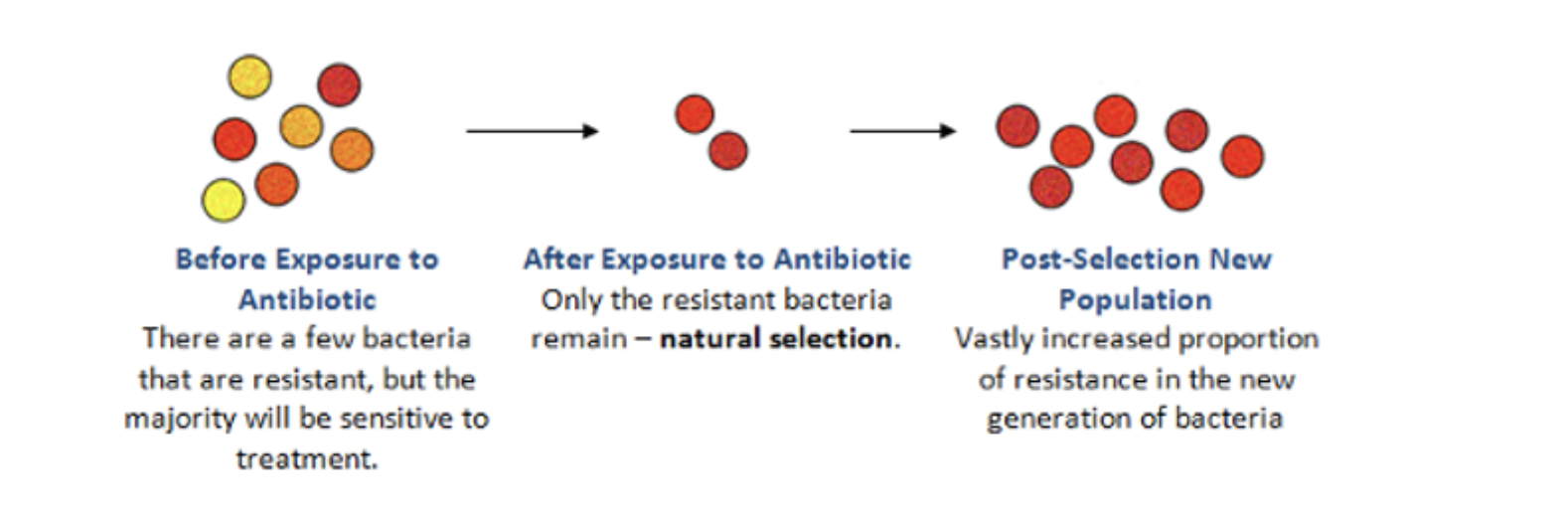
The black smoke seen being spewed from vehicles and factories is black carbon. Black carbon is a fine-particle, sooty material resulting from the burning of biomass such as wood. In developing countries, biomass burning is extremely common in everyday households as their cookstoves are typically composed mud and contain no ventilation (see Figure 1). By having no ventilation, the produced black carbon pollutes the air of the household and can create health problems and pose risk for those susceptible to sickness or with weakened immune systems. A transition from traditional cookstoves (TCS) to clean cookstoves that utilise liquid petroleum gas (CCS) rather than biomass is a mitigation measure crucial for reduction of black carbon emissions and is significant due to its greenhouse gas-like nature.
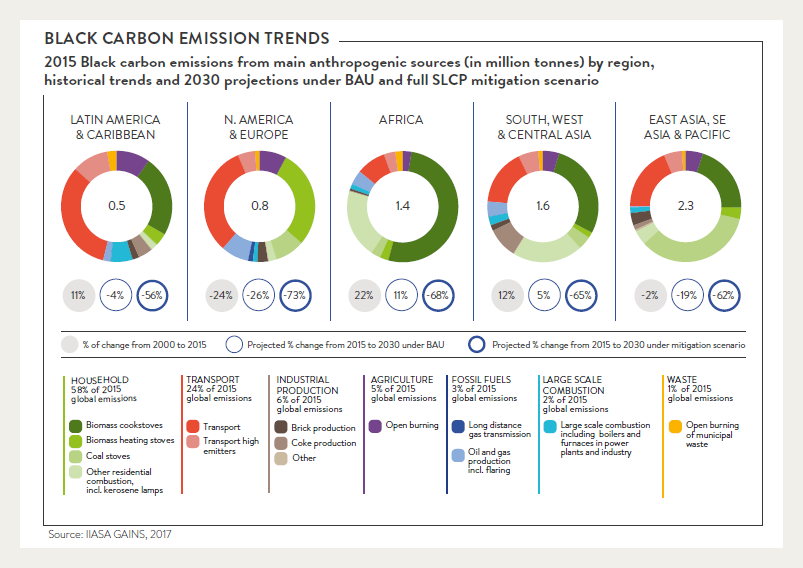
Figure 1. Image displaying emissions in continents of black carbon and their relative sources. Continents with greater amounts of developing countries have higher emission percentages. Source: IIASA GAINS, 2017.
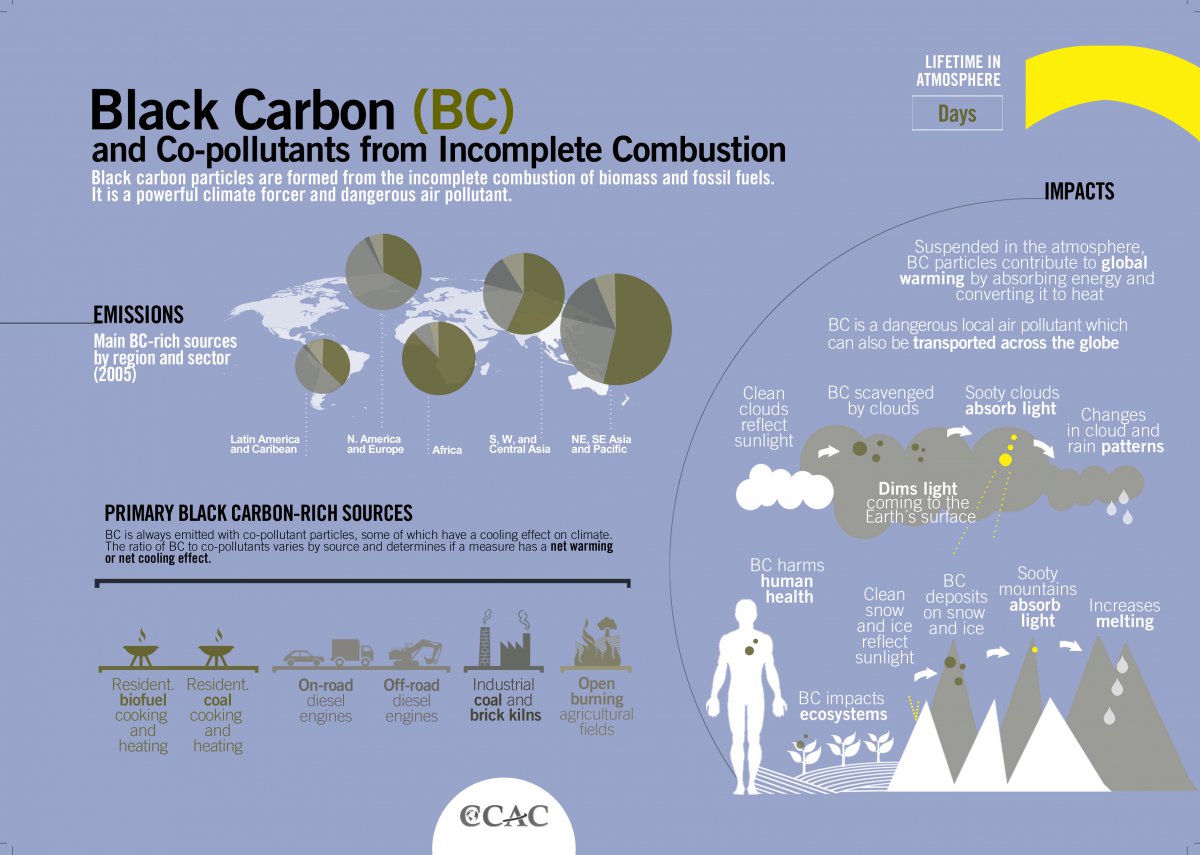
Figure 2. Figure displaying pollutants from incomplete combustion and burning of biomass as well as effects on the environment. Source: Climate and Clean Air Coalition, 2018.
Audio: Podcast showcasing the theoretical model created by our researcher as well as the relevance of these findings from the conduction of an interview.
Video: Embracing the change: cookstove transitions for health and global warming. Source: SCIE 300 Section 109 Group 5 | YouTube.
Researcher and the Significant Research
Abhishek Kar, the researcher interviewed, proposed a theoretical model called CI-CHANGE. This theoretical model combines various parameters such as social psychology and behaviour change. Through combination of various parameters, CI-CHANGE is more inclusive therefore can fit various households and their structures. Additionally, this theoretical model can provide potential guidance for actions to be taken at various steps of the acquisition process to maximise the number of cookstove transitions made and therefore reduce black carbon emissions.
Importance of the Model
Black carbon produced by the use of traditional cookstoves is the source of numerous fatalities caused by preventable diseases. Through use of this theoretical model, the conversion of cookstoves from biomass burning to gas will reduce the average black carbon pollution present in rural households. Because black carbon acts similarly to a greenhouse gas, heat from the earth is retained,, increasing global warming. The reduction of black carbon production due to cookstove acquisition will lessen the severity of its impact on global warming.
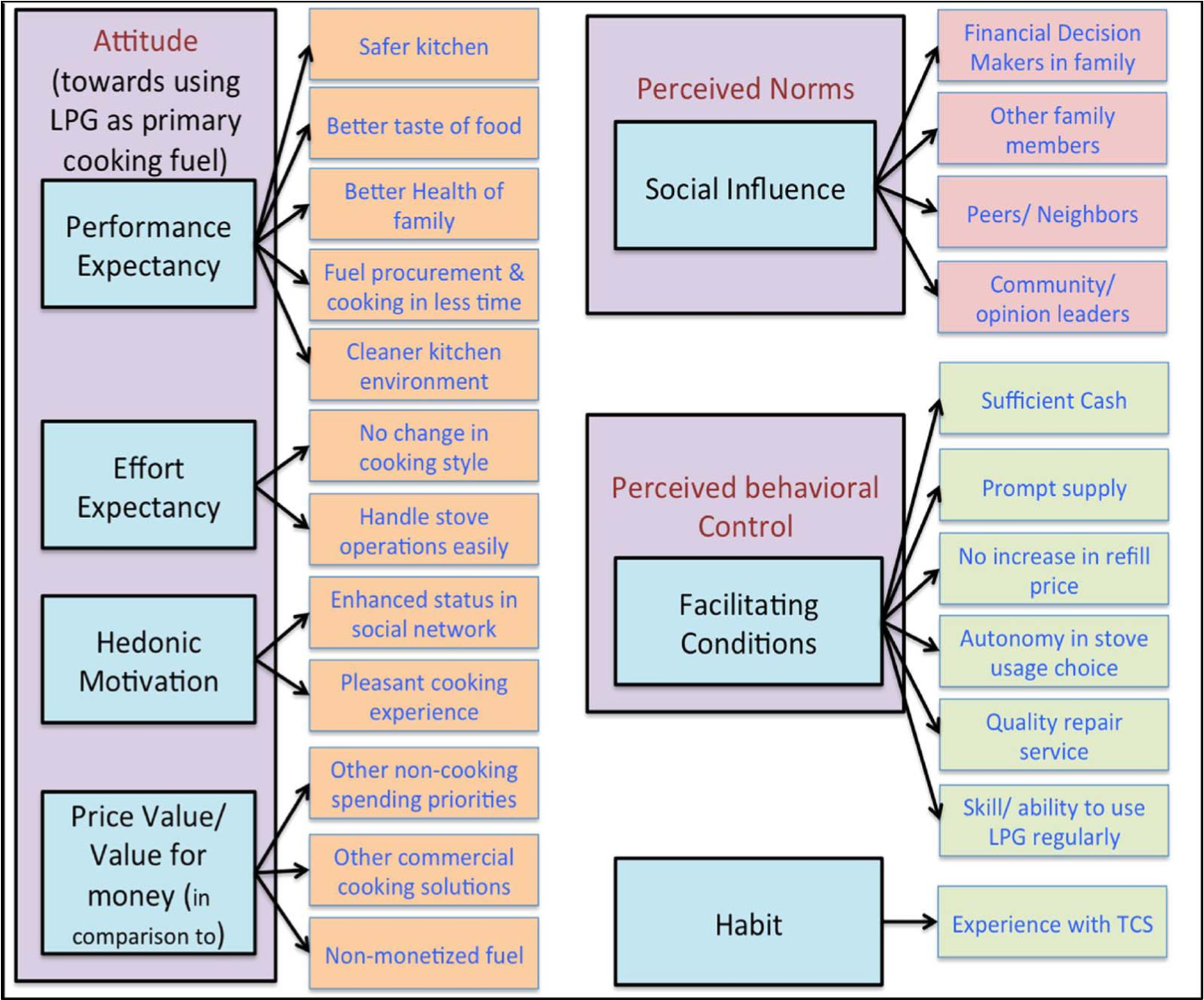
Figure 3. An outline of potential factors influencing cookware transition in rural community hierarchal households. Source: Abhishek Kar, 2018.
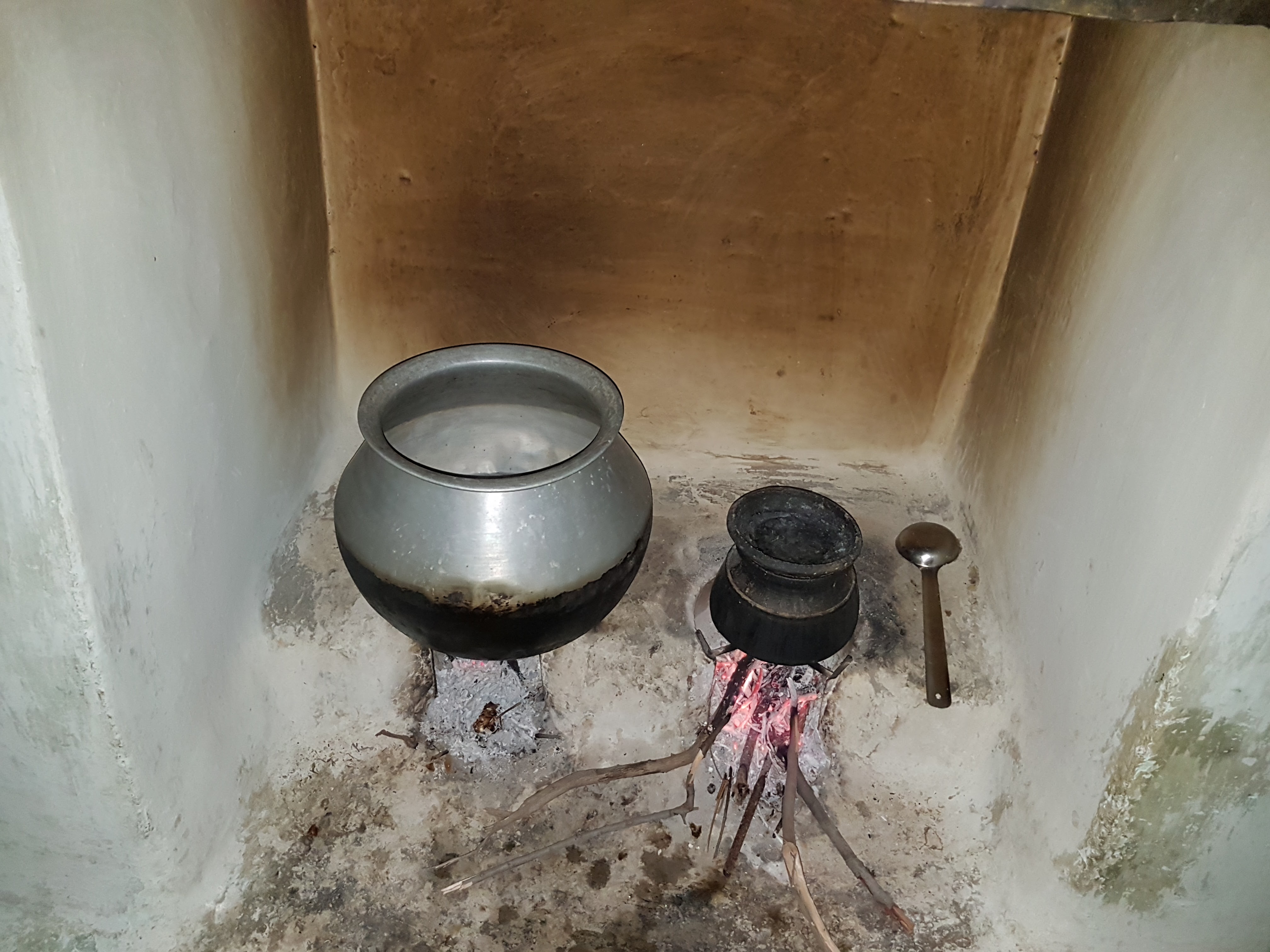

Abhishek Kar, 2012.
Figure 4. Image shows a typical traditional cookstove. It can be seen that n o ventilation exists, therefore the smoke and heat emitted from the stove have layered onto the wall. Source: Abhishek Kar
The importance of this theoretical model is additionally the gain of insight into the various influences affecting human behaviour change. With better understanding of these factors, researchers can further determine course of action to increase the conversion of cookware. Once these transitions are made, further steps can be taken to improve the health of households prior affected by this pollution. Furthermore, the creation of this theoretical model promotes further investigation of human behaviour change in situations with numerous influences.
-Vanessa Niedzielski, Jamaldein Adel, Jack Chen