Stroke is the most common neurological disorder and is the primary cause of physical disability. After cancer and coronary artery disease, stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States, with an incidence of at least 100 per 100,000 people. In Canada, there are more than 50,000 strokes a year. Every seven minutes, a Canadian dies of heart disease or stroke.
What is a Stroke
Stroke is also called the cerebrovascular disease which means it happens when blood flow to a certain brain area is cut off. Without the oxygen in the blood, brain cells start dying within minutes.
Here is a video understanding some basic concepts of stroke by an animated explanation.
Video Credit: HealthSketch
Types
There are two main types of stroke:
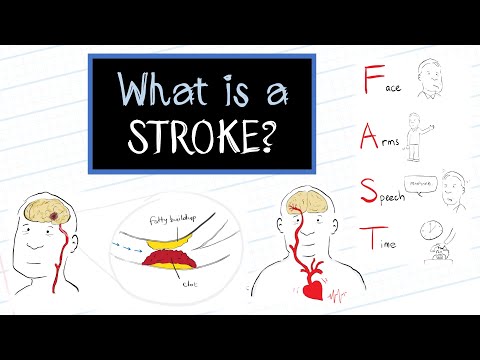
The first type is called Ischemic Stroke. Due to lack of blood flow caused by a blood clot or fatty deposits lodging within a brain artery. Approximately 85% – 90% of all stroke is due to ischemia.
The second type of stoke is the Hemorrhagic stroke, which is due to bleeding from a ruptured artery. It’s less common than an ischemic stroke, but it can be more serious. It can be a blood vessel in the brain balloons up and bursts, or a weakened one leaks.
Image Credit: FlintRehab
Causes
A common cause of ischemic stroke is the hardening of the arteries which is caused by plaques. Those plaques are mostly made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the arteries, leaving less space for blood flow. Therefore, a blood clot may stay in this narrow space and cause an ischemic stroke.
Risk factors that can be controlled include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, blood vessel disease, heart disease, smoking, obesity, high alcohol consumption, poor diet, etc.
symptoms
The F.A.S.T test helps spot symptoms of stroke:
Image Credit: sleepapnea.org
motor rehabilitation
At least 70% of people will survive a stroke, but they may have profound motor deficits. Most people lose their motor functions of the other side of the body (different from the side where stroke happens) after stroke. Thus, functional recovery through active rehabilitation training is essential to achieve increased independence and quality of life.
Muscle weaknesses are pervasive after a stroke. This can interfere with walking and other daily motor activities. Physical rehabilitation is an effective way to regain strength, balance, and coordination; whereas occupational therapy is essential for fine motor skills, such as using a knife and fork, writing and buttoning a shirt.
Stroke rehabilitation works the best after 24 hours to 48 hours of stroke occur. Most people make the biggest recovery during the first three months after stroke. By continuing exercising and practicing new skills help part of your brain take over new functions.
Here is a video talking about how Steve recovered his motor ability from rehabilitative technology after a stroke.
Video Credit: Mary Free Bed Rehabilitation Hospital
Elaine Yuling Chen