Have you ever imagined a robot being able to rebuild crime scenes using the clues and pieces of evidence it sees at the sites of crimes just like the character in the sci-fi game Detroit: Become Human? This is possible if the technologies of computer vision are developed and mature. Computer vision is the process that lets computers recognize, understand, and analyze pictures and videos. Computer vision is important because it provides the foundation for many science and engineering applications which will benefit humans in many aspects of their lives.
How does computer vision work?
The basis of computer vision is simple: computers transform an image into a set of pixels. Each pixel has a set of values which are used to represent the color of this pixel. Transforming images into data is easy, but it is hard for computers to categorize data in order to recognize objects. For example, it is hard for computers to recognize and understand which set of pixels represents a human face, a box, or a car. Therefore, computer scientists design different computer vision algorithms to help computers recognize objects in the pixel sets. Recently, in order to make computerized devices able to find similar patterns that allow them to recognize objects, computer vision scientists have trained their devices with numerous sets of images using machine learning technologies. (You can refer to my previous blog post to understand how machine learning works: click here).
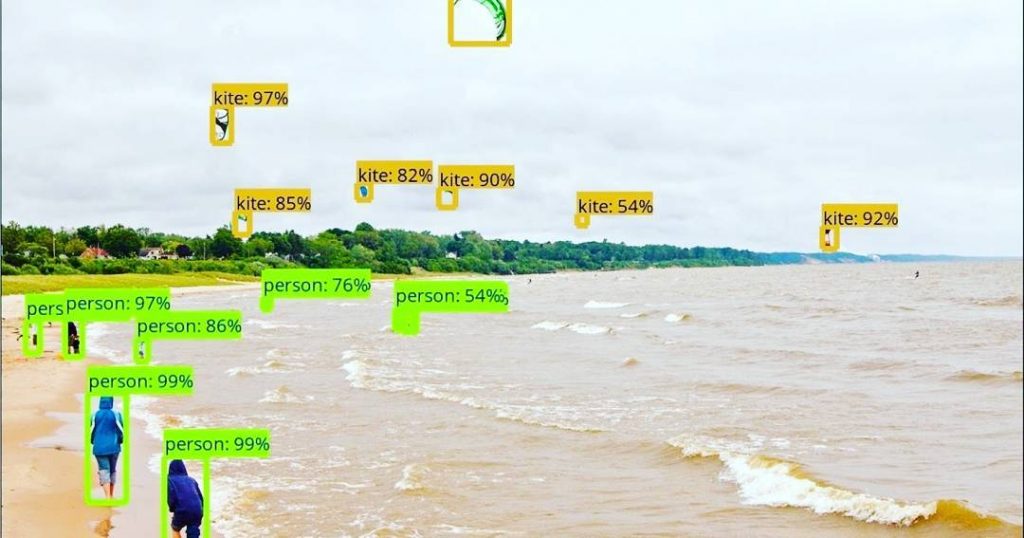

“The future of computer vision with the TensorFlow Object Detection API from Google. You won’t have to describe any photo….” by ShashiBellamkonda is licensed under CC BY 2.0. Source: flickr.com
What are some real-life applications of computer vision?

“Face Recognition Software Recognizes Animals Now Too” by terrykimura is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0. Source: flickr.com
You have probably already used a computer vision application in your life. For example, after you upload photos that contain your friends to Facebook, Facebook recognizes your friends and tags them automatically without asking you to tag your friends. This is done using Facebook’s facial recognition technology.
There are also a lot of other computer vision applications, such as barcode scanner and handwriting recognition. Also, check out the TED talk video below to see how we can use computer vision to transform our cities into smart cities.

Video: “How to use computer vision to improve cities | Nikhil Naik | TEDxYouth@BeaconStreet” by TEDx Talks. Source: youtube.com
Conclusion
Computer vision is a sub-branch of Artificial Intelligence because it studies the methods that provide computers with sight so that these computers can see the world just like humans. Nowadays, computer vision is a very hot research area in computer science. If you would like to take a computer vision course online, I recommend the Introduction to Computer Vision course by Georgia Tech on Udacity.
-Baihao Luo