Most people are monophasic sleepers, meaning we get our sleep all in one large chunk of the day. While there are some cultures that set time during the day for sleep , such as a siesta in Mediterranean cultures, most people (try to) get 6-8 hours of sleep at night, to stay alert during the day. To adapt to the busy schedule of school or work, polyphasic sleep schedules have become more and more popular with whole communities dedicated to the odd sleeping pattern.
Polyphasic sleep refers to any sleep schedule where you get more than 2 phases of sleep in a day.
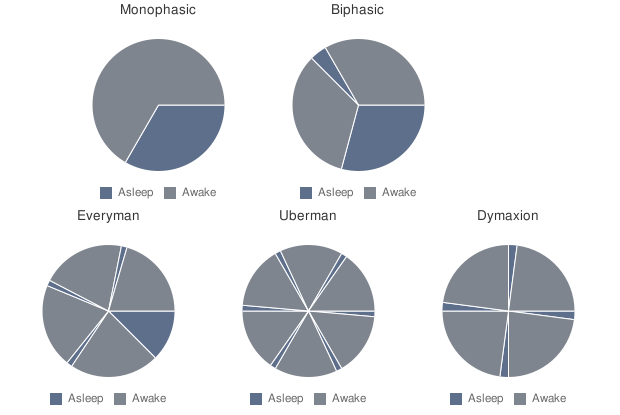
Source: http://polyphasicandexercise.blogspot.com/2012/06/polyphasic-sleep.html
By segmenting sleeping phases, polyphasic sleepers are able to sleep for much less in total, sometimes only 3 hours a day. This leaves more time to be productive during the day. There is a transition period from monophasic to polyphasic that takes a lot of dedication to change, and most say their alertness drops significantly during this time. Those who have successfully transitioned say that in general, they are just as alert as they were with a monophasic schedule, and they no longer need to sleep for more than 6 hours a day. Despite the anecdotal benefits, most people fail to transition, or return back to a monophasic sleep schedule shortly after a successful transition.
Most people will find it hard to transition and stay in a polyphasic sleep schedule, simply because their work and social culture doesn’t allow it. With everyone else being monophasic sleepers, it gets difficult to stay connected to others. It also gets difficult to find a place at work to nap during the day.
Aside from the mental difficulties people face with a polyphasic sleep schedule, sleep professionals find it difficult to recommend polyphasic sleep to people. As Dr. Avidan, director of the Sleep Disorder Center at UCLA, says, “There is very little data—none whatsoever in the medical literature—of carefully designed clinical studies demonstrating that polyphasic sleep has any advantage in human sleep medicine.”
Sleep is not like a bank account, it takes a full night of sleep to recover from just 1 hour of lost sleep. By shifting sleep schedules, you also end up shifting a lot of physiological functions that can cause adverse consequences for your endocrine and metabolic systems.
-Grant Li

