By Jia Liu
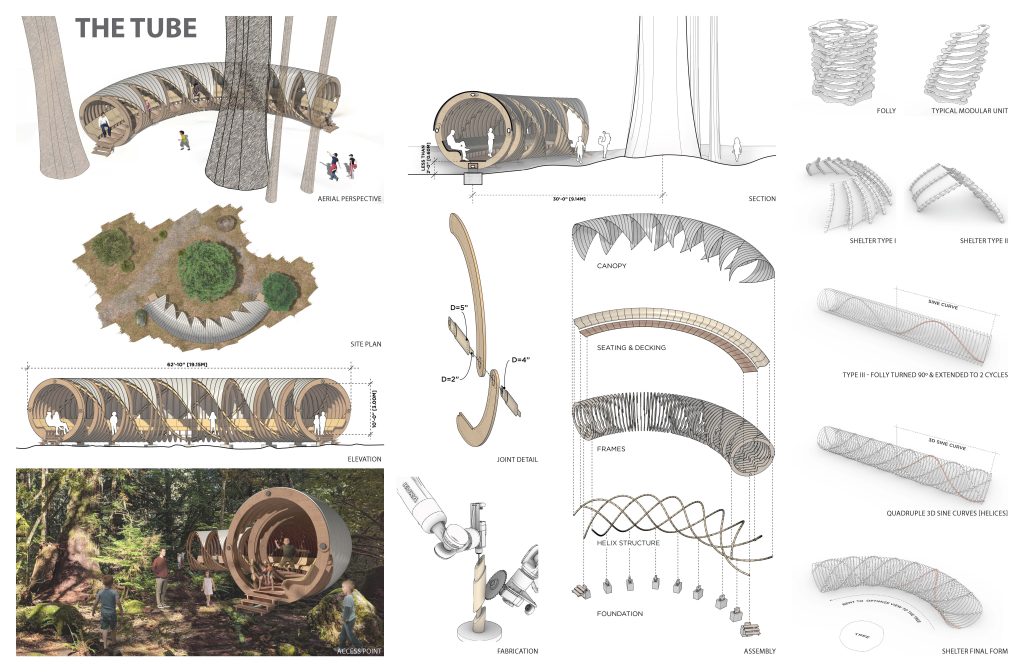
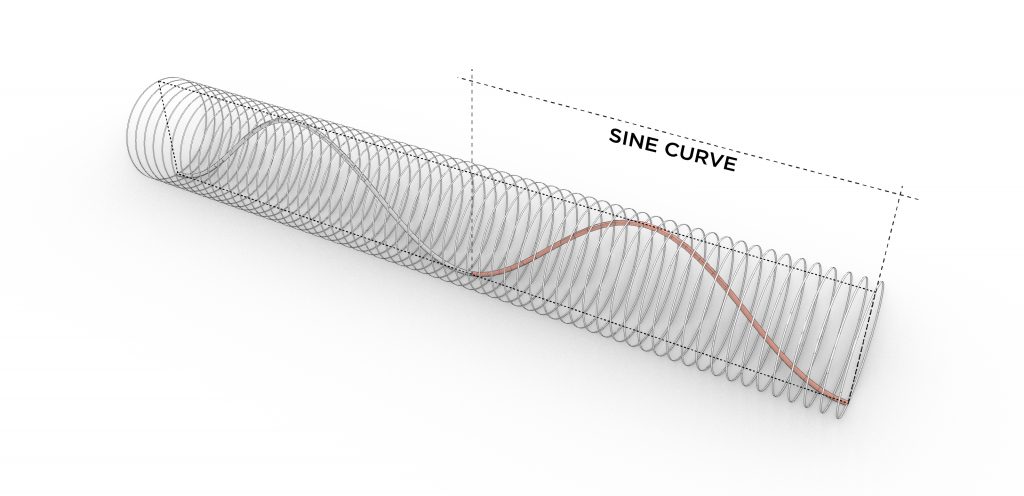
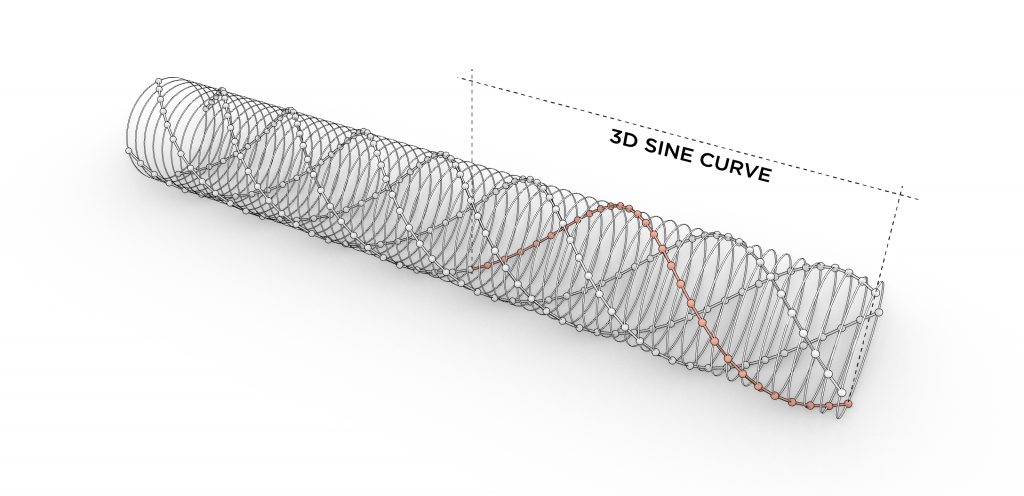
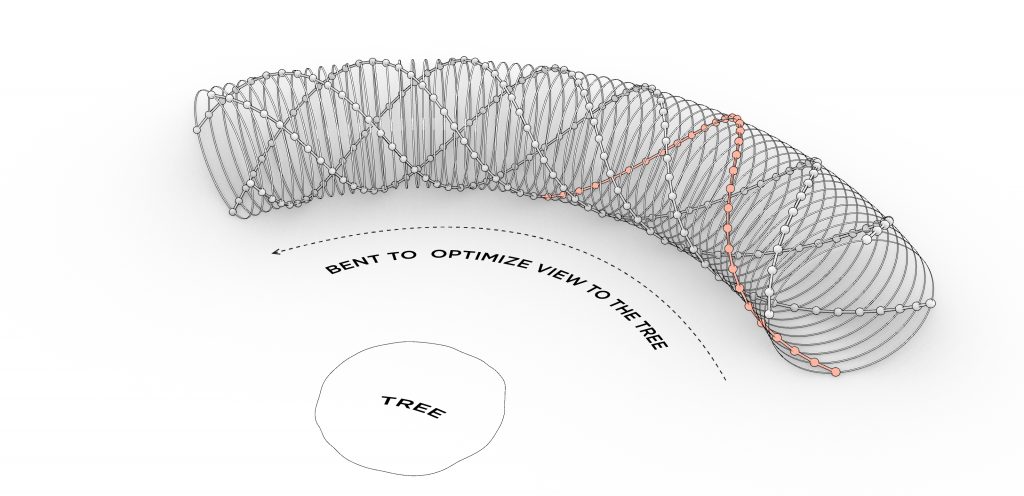
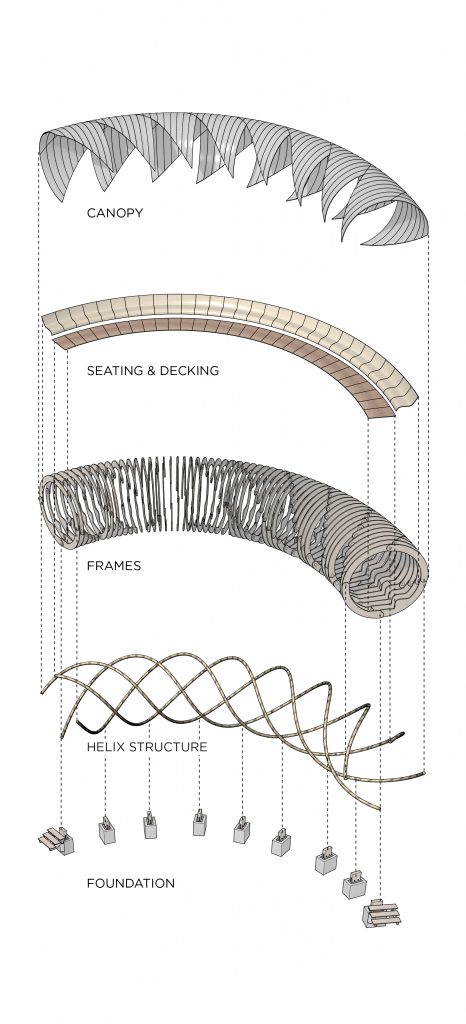
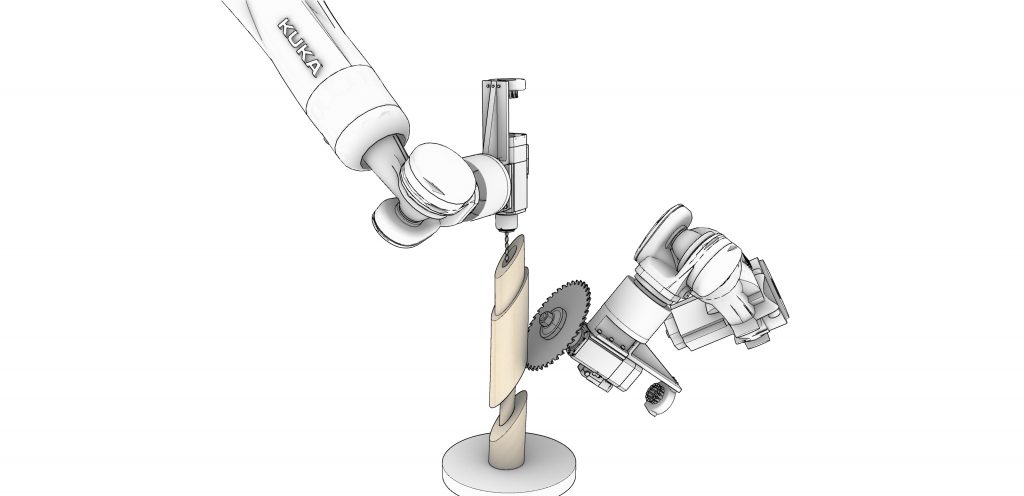
The typical modular unit of the folly system is comprised of two dowel-like primary elements clamping the arm/frame-like secondary elements. After exploring the potential forms that the typical joint can shape, the final shelter system has evolved into a tube-like self-supportive structure. The complex quadruple three-dimensional sine curves of the primary elements are derived from rotating and moving the joints along a linear path. Those three-dimensional arches start from the bottom and end at the bottom, forming a stable structure which is further supported by concrete foundation footings. The individual footings minimize the negative impacts to the root structure of the tree and have made it easier to level the deck on top of an uneven ground surface. The overall tube form has been bent and oriented to optimize the view towards the tree. The secondary frames contain carved out profiles for decking and seating elements. The frames are also strategically partially removed on the side facing the tree to allow easy access from the ground and help open up the view. The whole system is mainly made out of wood components with a metal canopy on top for weather protection. The shelter is placed 30 feet away from the tree to create more breathable space between the two and a better viewing angle. The tube form allows kids to run from one end to the other uninterruptedly, making it a fun experience with the shelter and the tree. The shelter itself is placed just off the main travel path in the forest to avoid blocking the circulation when the space is occupied. On the fabrication side, the frames could be milled using a CNC machine and the dowel-like component which has angled surfaces and holes could be cut by the robotic arm.