Researchers at the University of Texas have managed to cloak a three-dimensional object, essentially rendering the object invisible from all angles. This feat represents a major breakthrough in cloaking research, with previous studies having been either limited to two dimensions, or merely theoretical.
So, does this mean that Harry Potter’s invisibility cloak has become a reality? Not quite. This study was limited to working with waves at microwave frequencies, meaning that waves falling within the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum would still render the object detectable.
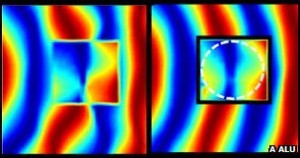
Left: Microwaves being blocked and scattered by object. Right: Microwaves being reconstructed by cloak. (Source: http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-16726609)
The researchers employed the use of plasmonic metamaterials—manmade materials with special light-bending properties. These metamaterials interact with light in a way that is opposite to that of ordinary materials. Our ability to see an object relies entirely on the process of light waves striking its surface and then reflecting back into our eyes. In the case of plasmonic metamaterials, waves striking their surface are scattered and reflected in a manner such that a “photo negative” is produced. This, in turn, results in the original waves being cancelled out, and it is this cancellation effect that renders the object invisible.
The process is similar to the way in which noise-cancelling headphones work. The headphones reduce outside noises by receiving them through a microphone, inverting them, and then playing the inverted signal back through the headphones. Since the inverted audio waves are completely out of phase with the audio waves coming from the listener’s environment, the two waves cancel each other out, significantly reducing the sound levels heard.
In essence, this study relates to the effectiveness of plasmonic metamaterials in cloaking real, three-dimensional objects in space. Although this study was limited to microwaves, the researchers hope to eventually extend their studies to work with waves in the visible light spectrum.


 (Artist’s concept of Kepler-22b from Kepler: Home Page)
(Artist’s concept of Kepler-22b from Kepler: Home Page)



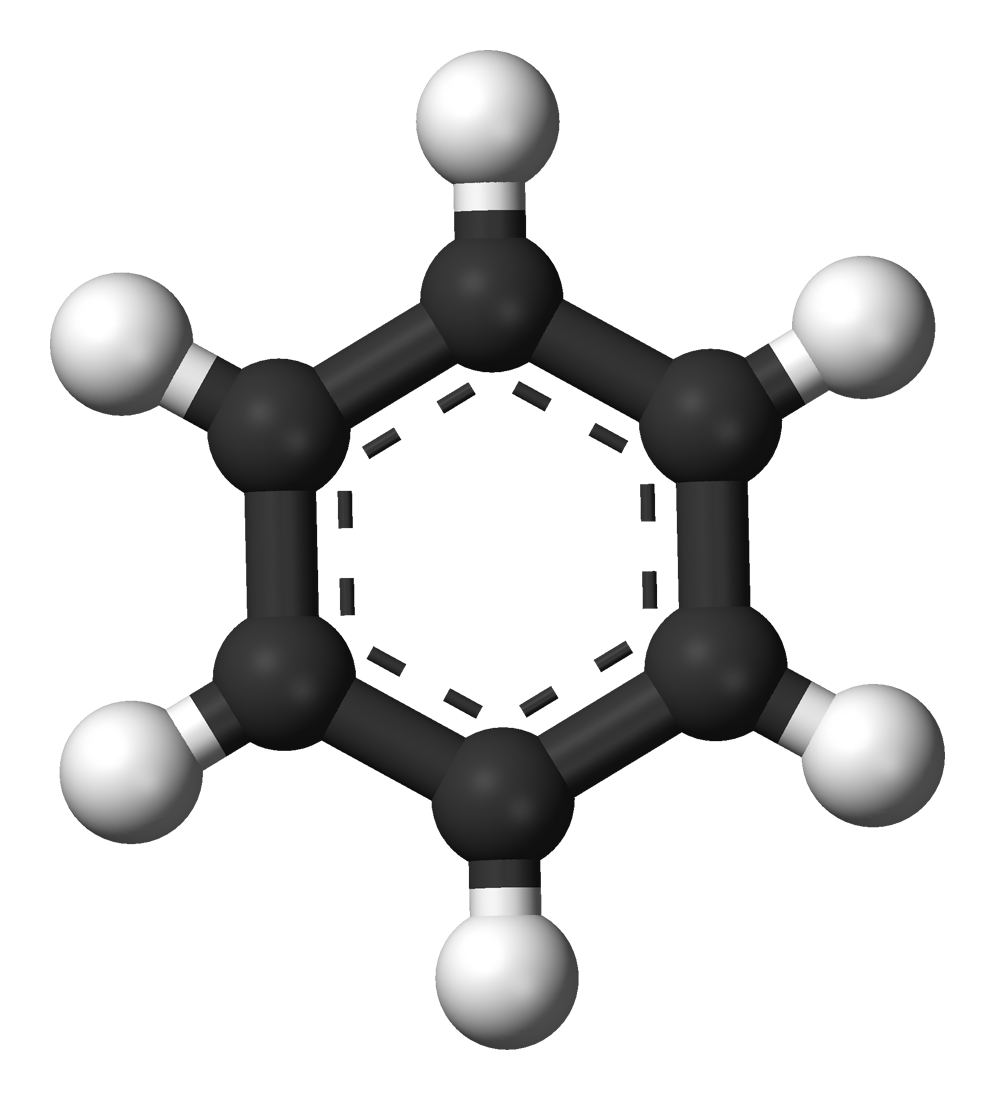
 Visible light of different wavelengths is detected by our eyes as a range of colors. Of the light that we can see, red has the longest, and violet has the shortest wavelength.
Visible light of different wavelengths is detected by our eyes as a range of colors. Of the light that we can see, red has the longest, and violet has the shortest wavelength.