Imagine this:
You’re living your life but suddenly you lose the urge to eat. Not a big deal, maybe it’s just a phase.
A week passes and you notice that those juicy arms you’ve worked so hard to grow seem to start looking like sticks. You face seems a bit discoloured, somewhere on the paler side. You weigh yourself, and you’re down 10 pounds. You start feeling a bit concerned but maybe it’s the keto diet that you started.
A few more weeks pass and you feel a small bump on your lower back. Now you’re freaking out and head to the hospital. After a diagnosis, the doctor says the three dreaded words: “you have cancer.”
What is cancer?
In the most general sense, cancer is a disease which causes cells to rapidly divide and grow uncontrollably and spread to different parts of the body. Cancer cells can also aggregate in certain areas and disrupt bodily functions, also known as tumours.
Current treatments for cancer:
Currently, there are three main types of treatment: surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. As surgery suggests, it is the physical removal of a tumour. Chemotherapy uses drugs to target to rapidly growing cells, even healthy cells such as hair. Finally, radiation uses x-rays, particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells. Of course there are other types of treatment such as targeted therapy but it is less used in the medical industry.
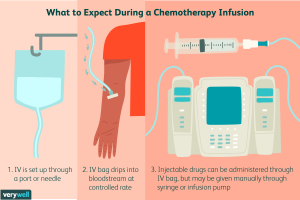
Example of Cancer Treatment (Chemotherapy) – Image by VeryWell
A newer type of treatment, car t-cell therapy:
Chimera antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a newer type of treatment that was tested back in 2010. Essentially, T-cells from a patient are extracted, genetically modified with CAR, and reintroduced into the patient. These modified T-cells are more adept at targeting only cancer cells. In a 2022 study by Melenhorst et al., it was found that two patients suffering from lymphocytic leukaemia entered remission right after treatment and after a decade, still continues to be in remission and even contains detectable CAR T-cells. This study shows that CAR T-cell therapy has it’s merits as being a legitimate treatment.
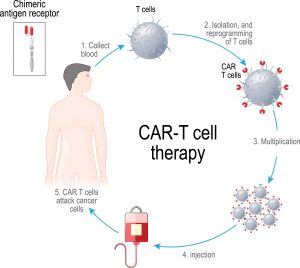
CAR T-cell Therapy Cycle – Image by Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News
Side effects of treatment:
Like all types of cancer treatments, there are some side effects associated. In a 2022 New York Times article by Gina Kolata, some side effects include high fevers, comas, and dangerously low blood pressure. However, some of these symptoms were resolved given time.
Overall takeaways:
Recent studies showing the results of CAR T-cell therapy has given it a chance to display the potential of it being a legitimate cancer treatment. Although some nasty side effects are associated with treatment, we cannot deny the positive effects it has shown. However, further research and testing would be crucial in developing this medical knowledge.
– Jimmy Huang
