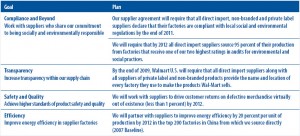
Procter & Gamble conducts primary qualitative online market research to aid its product decision-making process.
Related article : http://www.informationweek.com/news/development/tools/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=6507502
Main Article: http://hbswk.hbs.edu/archive/1476.html
I will use the Market Research framework (Class 15) to analyse P&G’s market research method.
1. Define problem/hypothesis
Senior executives could not answer simple questions about product functions -> P&G remained ignorant of how basic elements of its products were used/what aspects to capitalize
2. Determine research design
The Market Research Department was implemented. A vast team of researchers implemented primary qualitative research by asking detailed questions, focus-group-style.
Another unique strategy was assembling well-attired, natural door-to-door female interviewers to gain candid responses. They covered entire neighborhoods, and asked comprehensive questions about household products.
3. Identify data types and sources
Leader of MR campaign could give precise statistics about other companies.
4. Design data collection
Data collections improved in tande with improvement in communications technology.
5. Determine sample plan and size
Sample plans and sizes collected were similar throughout P&G’s history.
6. Collect data
Door-to-door interviewers collated specific data, even total recall in most cases.
7. Analyze
Detailed surveys distributed to focus groups allowed P&G to grasp product functions, competitor products and customer preferences.
8. Prepare report
Extensive reports adapted products/commercial messages to customers’ changing needs.
Meticulous attention to brand expectations, packaging, testing environment have resulted in highly satisfied customers.