To visualise the extent of damage of the BP oil spill : http://www.ifitweremyhome.com/disasters/bp

picture taken from : http://www.adannews.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/BP-oil-spill1.jpg

BP’s logo. The green and yellow colours and solar design highlight BP’s self-proclaimed duty to the environment
picture taken from : http://www.kolibriexpeditions.com/birdingperu/blog/index.php/bp-and-bird-conservation/

Greenpeace’s designed logo in response to BP’s oil spill
picture taken from : http://www.geeza.com.au/2010/06/redesign-bps-logo-with-greenpeace/
—
article taken from : http://blogs.forbes.com/csr/2010/06/15/bp-under-fire-profit-versus-responsibility/
Title of Article : BP Under Fire : Profit Versus Responsibility
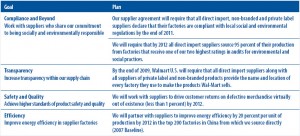
Being socially responsible means keeping global socioeconomic standards, respecting globalization, reducing global inequity and degradation.
The writer mentions that “It is possible to earn a profit and be responsible, but it is nearly impossible to do both perfectly.” However, BP shunned its responsibility by prioritizing its profit-seeking motive way above its social responsibility. Although it is natural for BP to prioritise profit-maximisation, it shirked its corporate (ethical) responsibility. With its previously strong international reputation and position, it could have implemented better safety protocol and avoided a poor safety track record.
This article does not give a comprehensive analysis, but other literature has shown up BP’s faults in light of being a global citizen. Reverse multiplier economic effects, massive unemployment in related industries and environmental destruction are severe implications. BP has also been hypocritical about its corporate values.
It is unfair to solely blame BP. Non-governmental organisations and governmental watchdogs should monitor multinational companies. However, most of the blame should still be attributed to BP considering its sheer size and power that it could have better utilised. Financial compensation is unlikely to alleviate the sheer extent of the destruction caused.