If you are like me, and have a hard time waking up in the morning, then you will definitely want to read this post.
A recent survey by Sleep Junkie found that just under 2/3 of people hit the snooze button at least once in the morning.

The majority of people hit their snooze buttons at least once in the morning. Source: Jam Loceng
You may hit the snooze button to get a couple more minutes of sleep, and then repeat several more times, thinking that those minutes will make you feel more rejuvenated. However, according to researchers, hitting the snooze button can actually make you more tired and less productive throughout the day.
When we go to sleep, our bodies follow the Circadian Rhythm, a 24-hour cycle which controls our sleep cycle and releases chemicals like melatonin, a hormone that makes you drowsy and sleepy. Melatonin production increases at night by a 4-step chemical mechanism in the brain and then decreases as you begin to wake up. During the night, your body enters REM stages (light sleeping/dreaming) before going into deeper sleep stages.
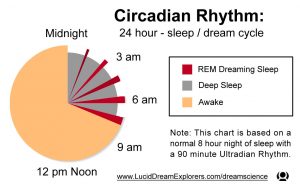
This graph shows the REM and deep sleep stages that occur during a normal, uninterrupted Circadian Rhythm. Source: Lucid Dream Explorers
What happens when you wake up, hit the snooze button and go back to sleep? Melatonin releases and your body restarts the sleep cycle, going from REM into deep sleep stages. When your alarm clock goes off again and you press the snooze button, you interrupt your body in the beginning of its sleep cycle, making you feel more tired and groggy.
This video by AsapSCIENCE shows the chemicals that are released both when you wake up and when you are falling asleep, and shows why you are tired and groggy in the morning.
I found these results really interesting because I hit the snooze button at least 3-5 times in the morning. So I decided not to hit the snooze button for a couple mornings in a row, and even though I felt tired right when I got up, I definitely felt less tired during the day compared to days when I constantly hit the snooze button.
However, researchers say that not hitting the snooze button won’t prevent you from being tired if you aren’t getting enough sleep. We mainly press the snooze button because we didn’t get enough sleep the night before.
This article by Business Insider shows the pros and cons of snoozing and that in certain sleep stages, hitting the snooze button will have a stronger negative impact. The worst case for hitting the snooze button is if you are overtired because then you are more likely to enter a deep sleep.
So next time you are about to hit the snooze button, stop yourself and see how you feel if you get up on the first try.
– Jessica Hasker












 Eczema, credit to
Eczema, credit to Scratching, credit to
Scratching, credit to 


