Have you ever wondered where does our carbon dioxide emission end up?. It turns out that oceans absorb 25% of our carbon emission.
As carbon dioxide enters the seawater, it reacts with water and carbonate ions, which decreases both the pH and carbonate ions concentration (Figure 1). This is known as ocean acidification.
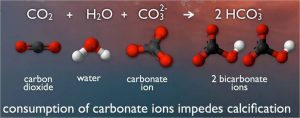
Figure 1. The chemical process of ocean acidification. Source: PMEL Carbon Program
Dr. Trional McGrath is a Chemical oceanographer from National University of Ireland. She has investigated ocean climate change since 2008 and she believes that the ocean acidification will increase by 170% in 2100!.
Why do we care about ocean acidification and how it will affect humans and living species in the water?. To test the consequence of this issue, researchers have placed a sea butterfly, which is an essential food source for many marine species, in a water with the expected pH of 2100 (Figure 2). They found that the sea butterfly’s shell dissolves in 45 days (Figure 3). Not only sea butterfly, but also many marine species, such as crabs, oysters, and corals need carbonate ions to build their shells. So, if the concentration of carbonate ions is decreasing, these species can no longer build their shells and they dissolve!.

Figure 2. Sea butterfly. Source: TED
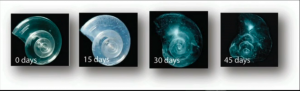
Figure 3: The shell of the sea butterfly dissolves in the expected 2100 pH. Source: TED
In addition, researches have also tested the effect of ocean acidification on tropical corals, which support a quarter of marine animals that are reef dependent. They found that they will dissolve in 6 months by the 2100. If the coral disappears, these reef dependant animals might not survive.

Figure 4: Tropical corals dissolve in a period of 6 months in the expected 2100 pH. Source: TED
Ocean acidification is a serious issue and it is directly affecting our ecosystem and our marine food chain. if we don’t reduce our carbon emissions, most of the marine species will extinct in the next century.
Renad Aldebasi