With the Canadian election race in full swing, some people know exactly who they are going to vote for, and others are unsure. Each of us have our own biases and opinions about the big issues like healthcare, defense, and the economy.
A group of scientists from the University College London just published a study in Current Biology that may show why “liberals are open to new experiences and can cope with conflicting information,” and why “conservatives are more sensitive to threat or anxiety in the face of uncertainty. ” (Quotes from Sciencedaily.com)
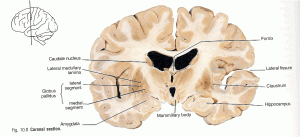
The team of researchers looked at the different sizes of these two structures called the anterior cingulate cortex and the amygdala (click the name to find out more information about each structure from Wikipedia). This team suspected that there might be a structural difference in the brain that accounts for these differences. And this is indeed what they found. People with larger anterior cingulate cortexes tended to have more liberal views. Whereas people with larger amygdalas tended to have conservative views.
But there is not enough evidence to conclude that only these structures account for the political differences. There were too many uncontrollable factors to take into account, such as life experience, family history, also what kind of environment the subject was raised in. And people also have the ability to change their views over time.
Ryota Kanai of the University College London concluded in the article that “It’s very unlikely that actual political orientation is directly encoded in these brain regions,” and “more work is needed to determine how these brain structures mediate the formation of political attitude.”
Side note:
Vote Compass is a free online survey where just click the answers that are closest to your opinions and it will tell you which political party you are closest to. I think it’s pretty cool, to check it out click on Vote Compass to go there now.
DON’T FORGET TO VOTE!