By: David Sawatzky, Paula Samper, Moh Mehrabi, and Daniel Passaseo
There is a new drug that can target and block harmful metal ions in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. This drug developed by Dr. Chris Orvig from the University of British Columbia, is known as a chelating drug, which means it grabs hold of its target and makes it unable to do more damage. This is a massive breakthrough for treating Alzheimer’s disease, for which there is no cure.
This research is very important because you can only treat the symptoms of Alzheimer’s, and the leading treatments do a very poor job and targeting the affected brain cells. Dr. Orvig’s model drug has a sugar molecule to help deliver it to the brain. It is a very innovative idea, and there have been no previous Alzheimer’s drugs that are effective at getting the drug into the brain.
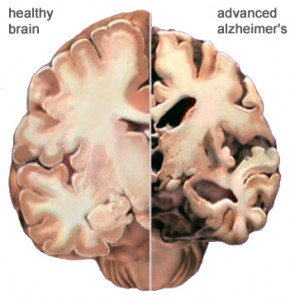
One of the effects of Alzheimer’s is neurodegeneration, which means the brain cells die. As these brain cells die, the patients lose their memory and motor skills, making it hard for them to live on their own. These patients then require family members and or caregivers to help with daily activities like preparing food and bathing. This takes a large emotional and financial toll on the patient’s family.
The actual causes of the disease are not known very well, because there may be many factors that contribute to this disease. But it is known that Alzheimer’s is not genetically inherited, although some genes may contribute to the risk of developing Alzheimer’s. For more information about what causes Alzheimer’s disease listen to our podcast!
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
The following video does a great job summarizing Dr. Orvig’s research and what Alzheimer’s disease is all about.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VTrjcV_EyfI
There is hope that research like Dr. Orvig’s will eventually lead to a better understanding of this disease and eventually a cure.