The first step we wanted to take in our research is to identify those who were the most physically vulnerable to COVID-19. In this project, we considered age and exposure to air pollutants as the major factors that determine the at-risk population in terms of physical health. The population was divided into four groups: 50-59 years old, 60-69 years old, 70-79 years old and over 80 years old. As for air pollutants, we examined residents’ exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
To make an integrated analysis on above factors, we conducted Multi-Criteria Evaluation (MCE). CHASS provided the 2016 census data and a shapefile of the transportation network was downloaded from Statistics Canada.
MCE for Age Groups
Location quotients (LQ) were calculated for each factor to identify dissemination areas (DAs) with higher levels of at-risk groups. LQ is the ratio of the percentage of a given age group in a DA to the percentage of that age group in the whole city of Vancouver. For instance, in DA59150701, there are 530 people over the age of 50, of whom 30 are over the age of 80. In Vancouver, there are 633,125 people over the age of 50, of whom 27,525 are over the age of 80. Therefore, the LQ value of people over 80 years old for this DA calculated is:
LQ = (30/530)/(27525/633125) = 1.30.
If the LQ is greater than 1, the DA has a disproportionately larger share of a particular group of age. We would therefore look at these LQs and normalize those with values of 1 and below to 0. The normalized LQ data were joined to the DA layer and then converted into raster layers for each age group.
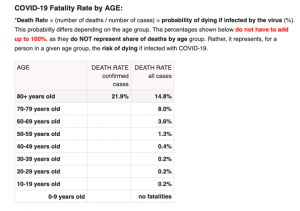
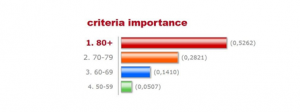
Taking into account the different responses to COVID-19 in different age groups, we weighted it according to the respective mortality rates provided by New York City Health as of April 14 (Figure below). The death rate shows the risk of dying if infected with COVID-19, for a person in a given age group. Weighted importance of each of the four factors was chosen using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). After comparison of each factor, the weights are as in Figure 2. The final weighted map was then created using Weighted Sum.
The final weighted map was then created using Weighted Sum.
* There was uncertainty involved in this step. The 80+ age group is 11 times more important than the 50-59 age group, but we set the importance index at 9 because it is the maximum on the AHP calculator.