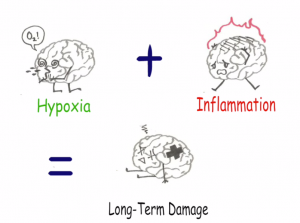
The first step to treating a disease is to catch the culprit behind it. Researcher Jingfei and her team set out to do just that and discovered that hypoxia (a lack of oxygen) and inflammation act as partners in crime to cause damage to the brain.
Jingfei’s recent publication from the University of British Columbia (UBC), highlighted the key role that hypoxia plays in brain damaging diseases such as Alzheimer’s, something that has been overlooked in past studies. They found that hypoxia and inflammation combined is what causes long term damage to the brain.
“This is a never-before-seen mechanism among three key players in the brain that interact together in neurodegenerative disorders,” says Jingfei’s supervisor, Brian MacVicar, from the Djavad Mowafaghian Centre for Brain Health at UBC. The three key players that he is referring to are hypoxia, inflammation, and microglia (the immune cells of the brain).
By manipulating the brain slices of rodents using various techniques, the researchers tracked the movement of microglia and found that the two factors, hypoxia and inflammation, work together to permanently weaken the connections between brain cells. Furthermore, the damaging effects of the two factors may worsen people’s memory, which is one of the early symptoms of brain diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Pictures (or rather videos) are worth a thousand words so watch below to see exactly how they went about conducting this exciting research and what they found.

(Video: Credits to Ian, Siana, Shikha, and Sean)
So, who will benefit from this research? Jingfei said, “Well I think right now it still will be researchers, because this paper is more like a new finding of something people didn’t know before, so hopefully […] they can build more realistic model on top of it.”
Moreover, some researchers have already built upon her research in the short time that has passed since her paper was published. Researchers at Cambridge University have broadened our understanding of microglia in a recent study. They found that microglia are not just important after injury to the brain, but also for daily functioning.
In another study, researchers looked at human brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s to see if they’re related to inflammatory conditions in multiple sclerosis (MS). They found that the type of inflammation found in brain diseases is completely different from the inflammatory conditions in MS.
At the rate that research around the world is being conducted, we can only hope to see clinical applications in the near future that hopefully bring us a step closer to finding a cure for brain diseases.
We can do our part in helping researchers gain more support in their studies by raising awareness of brain diseases. It’s important for people to be aware of these diseases and realize how devastating they can be to the patient, and their loved ones.

Participants of Walk to End Alzheimer’s 2014. (Flickr Image: Yooperann)
Below is our “Myth or Fact” podcast that aims to raise awareness for Alzheimer’s, which affects over 15% of Canadians over the age of 65. Listen to find out just how much some of the brightest students at UBC know about Alzheimer’s.
https://soundcloud.com/e-thereal-1/so-project-podcast
(Podcast: Credits to Ian, Siana, Shikha, and Sean.
Music: Credits to House Theme Song from YouTube User: Damaster00777)
No copyright infringement intended
– Written by Ian, Siana, Shikha and Sean