As nuclear generators around the world continue to produce large volumes of nuclear waste, scientists and engineers are scrambling to find a way to deal them. Dr. Ramana explores the various issues in handling nuclear waste in his paper.
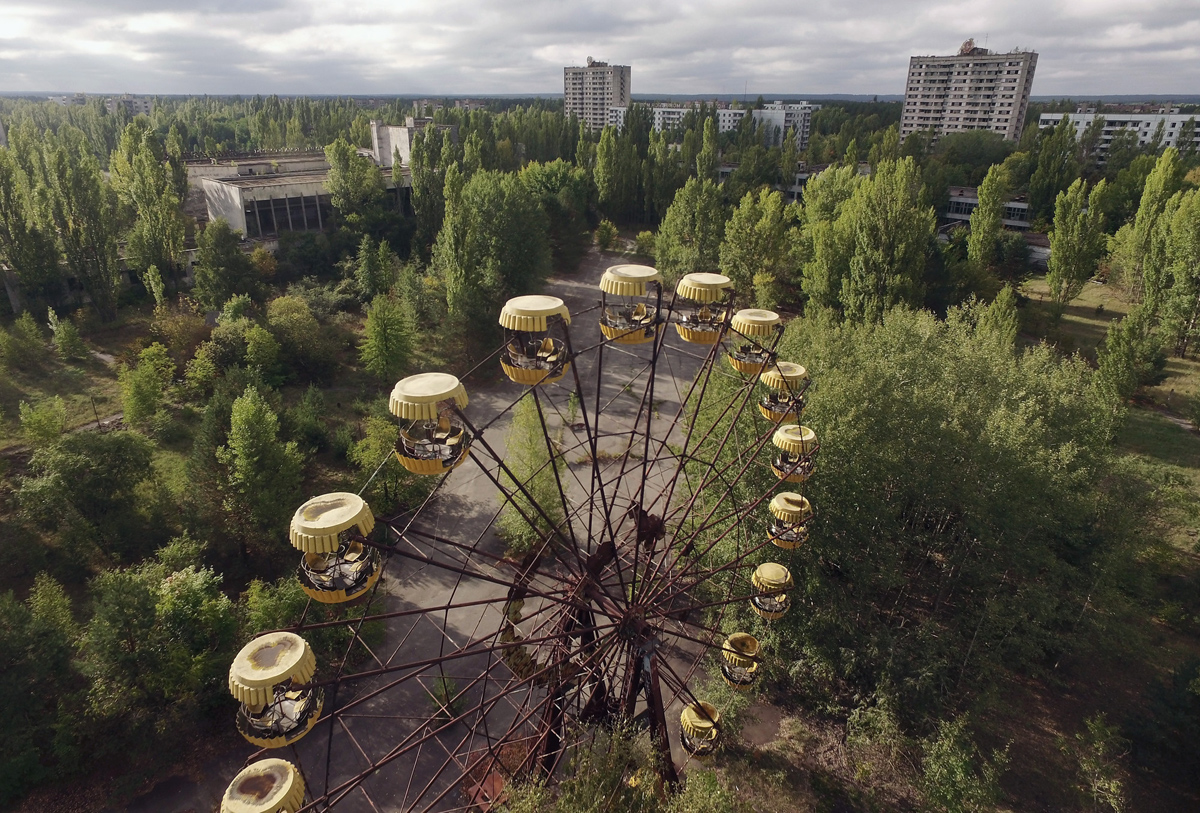

One of the most iconic and unsettling images of Chernobyl 30 years later. Photo Credit: The Atlantic
In the process of creating nuclear power, uranium is put into high energy generators where the atoms are split through a process called fission. The resulting byproduct is an extremely hot and radioactive waste called spent fuel. Currently, the only existing solution is to dig deep holes and isolate this waste in what are called geological repositories. However, we have learned that these repositories themselves present a slew of issues.
This video discusses the technical issues of nuclear waste with UBC’s nuclear energy specialist: Dr. Ramana.
The first issue is that the waste remains radioactive for up to one million years. In order for the spent fuel to remain safely isolated, engineers have to construct a canister capable of containing the waste for the entire duration. Furthermore, as most metals are susceptible to rusting, the repository site must somehow remains dry for the entirety of the decay period.
Assuming that the aforementioned complications can be dealt with, the waste must then be transported from the nuclear generators to the repository. One can expect accidents to occur during this transportation period. In 2014, a drum exploded at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plan (WIPP) location in New Mexico. This incident was caused by a seemingly minor mistake, yet was one of the costliest accidents in U.S. history.
The next concern comes with selecting the actual location for the geological repository. Seeing how there are currently zero running geological repositories, the governments have had a 100% fail rate at convincing residents why they should want to live near a nuclear waste facility.
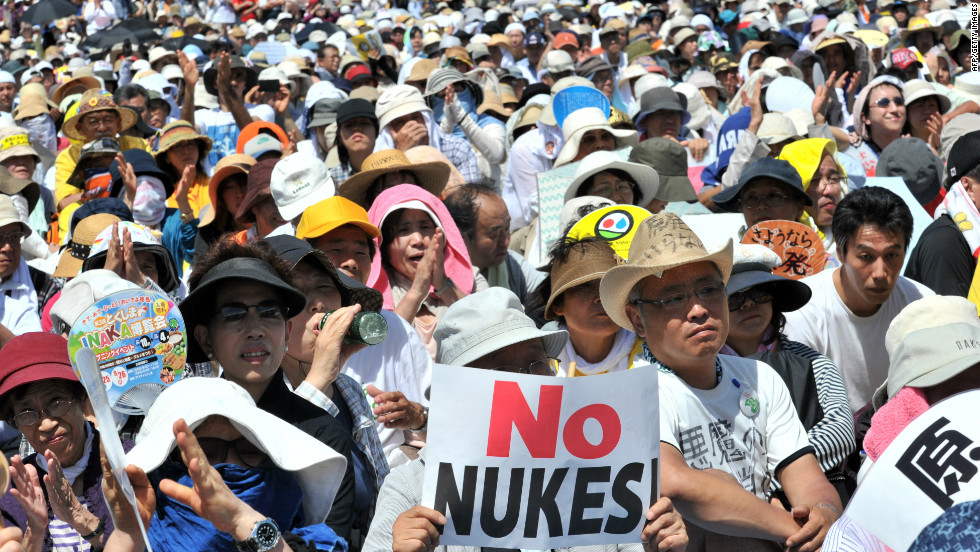

10,000’s people protest nuclear energy in Japan. Photo Credit: CNN
Dr. Ramana stated that the only effective solution to this nuclear waste problem is to phase out the usage of nuclear energy entirely. As mentioned in his paper, Will Rogers states, “If you find yourself in a hole, stop digging.”. Initially, nuclear energy was a means to reduce carbon emissions. However, it has become clear that this solution has created more issues than it solves.
“Electricity is but the fleeting byproduct from atomic reactors. The actual product is forever deadly radioactive waste.” – Kevin Kamps, Environmental activist
Even for the most brilliant scientists, designing an operational canister has been a fruitless endeavour. Dr. Ramana mentions during the podcast that the greatest misconception regarding nuclear waste is that people think they can just “wish away” this inherent, radioactive property of spent fuel. In B.C., more than 85% of our electricity is sourced from hydro-dams. In fact, we produce so much electricity that we export it to the states and rest of Canada.
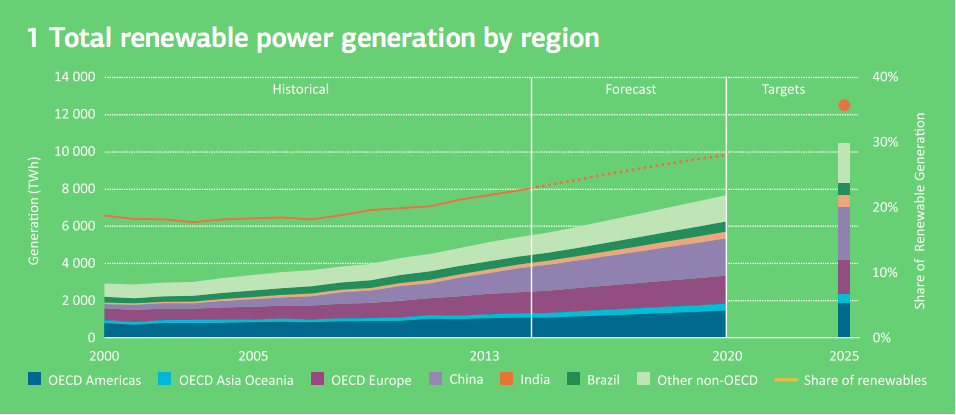
Renewable energy trend and forecast. Photo credit: International Energy Agency
Rest assured, with hydro, solar and wind options becoming cheaper and more readily available, the global usage of renewable energy sources is on the rise. It may be possible that Dr. Ramana’s idea of a world without nuclear energy is something we may get to look forward to.
Written by: Julia Lee, Jerry Chen, Anna Han, James Wang

