Hello Team Peanuts,
The post below is my assignment 1.3 regarding our practice on writing definitions. The term I have chosen is heuristics. In the context of psychology, this term is used when one is describing the difference between making rapid and almost reflexive decisions versus making slower yet more thorough decisions.
Term: Heuristics
Parenthetical definition: Heuristics (our intuition) are often used when we need to make quick decisions.
Sentence definition: Heuristics are our mental shortcuts that enable us to make quick and reflexive decisions on a day to day basis.
Expanded definitions:
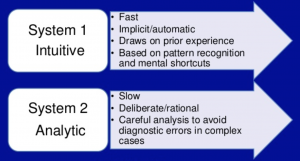
The term heuristics originates from ancient greek word. The term heuristics is an irregular form of the greek word heuriskein, which means to find or to discover. This concept was first named as satisficing by Herbert A. Simon when he conducted research on human decision making. However, eventually it was found that a similar concept had already been explored in ancient Greek research and had a term called heuriskein. With more research on this topic, researched eventually coined the term as heuristics. This term is to be understood within a broader concept of the Dual Process Theory. This theory states that in decision making, there are two separate systems that could be employed. The first system is our intuition, which means decisions are subconscious and automatic. The second system is our reasoning to which we would use conscious thoughts to make calculated and deliberate decisions. Specifically, we often use heuristics to aid our intuitive decisions. Therefore heuristics is present in the first system and not used when making reasoned decisions.
References
Cherry, K. (2019, June 17). How Heuristics Help You Make Quick Decisions or Biases. aaRetrieved from https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-a-heuristic-2795235
Heuristics – Explanation and examples. Retrieved from aahttps://conceptually.org/concepts/heuristics
Parvini, N. (1970, January 1). Key Concepts: Dual-Process Theory, Heuristics and Biases. aaRetrieved from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1057/9781137543165_2
Manesh, R. (2017, December 7). Dual Process Theory Case 2. Retrieved from aahttps://www.slideshare.net/RezaManesh3/dual-process-theory-case-2
Leave a Reply