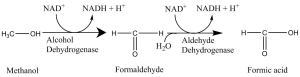Why after drinking, some people’s faces will turn red, while some of the others turn white?
Let’s talk about the reason for blushing first. Many people think this is caused by alcohol. But, it is instead caused by acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde has the function of expanding the capillaries, and the dilation of the capillary of the face is the reason of blushing. So if some people drink and blush, it means that they can quickly convert ethanol into acetaldehyde, which indicates that they have efficient ethanol dehydrogenase to complete this conversion. Relatively, there is another enzyme called aldehyde dehydrogenase. People who drink with red face are because they only contain ethanol dehydrogenase enzyme, but not aldehyde dehydrogenase. Therefore, the body rapidly accumulates acetaldehyde and cannot metabolize. As a result, the red face may last for a long time. Generally, the red colour will disappear after one or two hours. This process depends on the cytochrome P450 in the liver that slowly converts acetaldehyde into acetic acid, and then goes into the Krebs cycle and be metabolized.
What about people who can drink a lot? Usually, for this kind people, the more they drink, the whiter their face are. For one thing, they will suddenly fall into a blind drunk degree. That is because the highly active ethanol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase are not presented simultaneously, mainly due to the slow oxidation of P450 in the liver. So, why are such kind people able to give others a feeling of they are “wine tanks” ? The reason is: they rely on inner body fluid to dilute alcohol. It suggests that the bigger they are, the more they can drink. Until alcohol levels exceed 0.1 percent, under normal circumstances, they will fall into a coma.
What happens if a person has a highly active alcohol dehydrogenase and a highly reactive acetaldehyde dehydrogenase? Then we can say that he/she is a “wine tank”! We can judge if a person is a wine tank or not by seeing if they will sweat profusely while drinking. Because if both enzymes are highly active, alcohol quickly becomes acetic acid into the Krebs cycle, then turn to heat and sweat in a very short time.
People who have a white face after drinking are more likely to injure their liver. They lack the signal of drinking baseline, so it is easy to drink beyond their ability, which makes them drunk. What’s more, the alcohol in their bodies accumulates in the absence of highly active enzymes, leading to liver damage.
Depending on the introduced after-drinking characteristics, it can help you understand your own drinking system. Drinking according to your physical condition is a good method to protect your personal health when enjoying alcohols.
-Olivia Yang-