Just yesterday, scientists announced that a baby who was born infected with HIV was cured of the disease. The doctors diagnosed the mother to be HIV-positive at the time of labor; the baby was at a high-risk of exposure to HIV, and later confirmed to be infected. After 30 hours of birth, the doctors treated the baby with highly active antiretroviral therapy or HAART, a combination of 3 antiretroviral drugs in order to prevent HIV from making home in the baby’s immune cells. The baby was given treatment for 18 months, and half a year later from quitting treatment, its blood showed no sign of infection.
This is the second case of curing the infected of HIV. The first person to defeat HIV is Timothy Brown who received bone marrow transplant from a donor with HIV-resistant genetic mutation, which is found in 1% of European population.
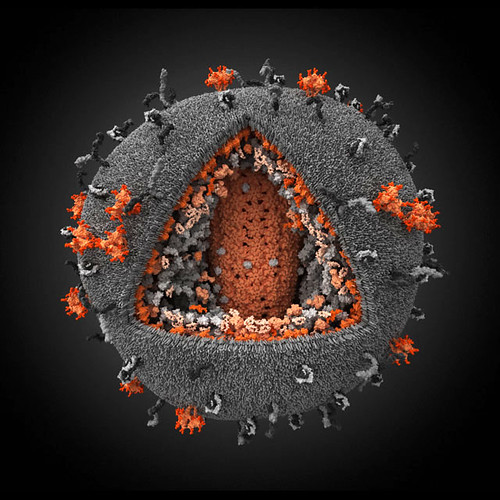
HIV via flickr user: Microbe World
This “breakthrough” may bring hope to children born with HIV, whose number count to 300,000 worldwide in 2011, and comprise about 1% of HIV patients. However, mother-to-baby HIV transmission is 99% preventable if the mother is treated during her pregnancy. Given that most babies with HIV are born in developing countries where only 50% of pregnant women have access to the medicines, it is crucial to urge wealthy countries to increase their support to organizations such as UNAIDS that work for the elimination of mother-to-baby HIV transmission.
HAART is not a cure for HIV patients at later stage of infection as it can only suppress the virus from replicating rather than killing the viruses themselves. Nevertheless, the news of world’s second case of curing HIV gives hope that the virus may be conquered if actions are taken quickly.