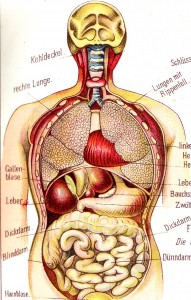
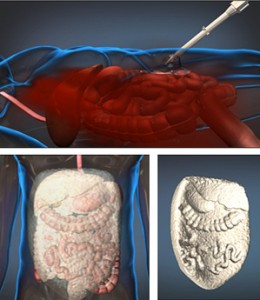
The need for organs for people suffering from disease is ever-growing, and high.
This need has resulted in large scale ethical debates, some doctors opting for more radical ways to harvest organs. At the same time, patients are dying because they were not given a transplant promptly. The current situation in North America is dismal at best.
However, hope does exist! A recent innovation reported by a group of researchers at Heriot-Watt University could solve the problem. How you might wonder? By what scientists are calling “organ printing“.
Organ printing is a technology combining the concept of 3-dimensional printing and stem cells. A 3-dimensional printer is a machine that is able to make 3D objects when given some sort of electronic plan for the object to be printed. Traditionally, 3D printers have used metals or plastics as the ink for making objects. But instead of metal or plastic, an organ printer uses embryonic stem cells as ink; cells that are able to divide and change their identity into any other cells such as heart, lung, kidney or even brain cells, and carry out their function.

A printer that uses cells as ink could make organs! Pictures adapted from Seahen, Jomegat and Osnimf (left to right) via Wikimedia Commons.
You might wonder why this would be considered a huge breakthrough. The discovery of stem cells heralded a large amount of attention. We initially believed that we would be able to grow organs easily; however, over time, we learned that stem cells are more complex than we realized. Stem cell growth is difficult to control. Even though we can currently make a stem cell change its identity into a cell we want it to be, we cannot effectively mesh groups of cells into highly organized layers, like how complex organs such as the heart and kidneys are laid out. Experiments reported as late as three years ago could only make balls of different cell types from stem cells using chemicals. 3D printing using stem cells allows us to organize cells and distribute them the way we want them to be, and so, we could make complex structures with different layers in a consistent way in the near future.
Below, Dr. Anthony Atala talks about organ printing techniques he is researching in his lab.

By CNN via Youtube.
But how near is the near future? I remain skeptical. Stem cells are complex things, and we have much to learn about them. Just because we place them in the right positions in the right type does not mean that all problems will be solved. Additionally, we have yet to research where to place cells so that they function the right way in an organ. I would think that this technology would take at least 10 years to be relevant to our everyday lives. Only time will tell.
-Shaun