The person sitting beside you in your morning lecture is slurping down an extra-large iced cap, with whipping cream AND chocolate drizzle. Those french fries in the cafeteria at lunchtime are looking deliciously tempting, and when you get home from your long day your roommate has a fresh batch of chocolate chip cookies sitting on the counter.

Chocolate Chip Cookies! Christie @ Love From the Oven via Flickr Creative Commons.
Oh the temptations, but with “beach season” soon approaching, it makes for a hard choice between those deliciously fattening foods and a trim waistline. What if I told you that soon, you may be able to indulge in all of your favorite foods, never hit the gym, and still turn heads in your swimsuit this summer?!
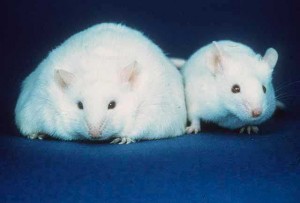
Genetics researchers at the University of Colorado’s School of Medicine, led by Professor James McManaman, have recently discovered a gene that appears to be directly related to obesity. This gene, called Perilipin 2 (Plin2), produces a protein that plays a key role in regulating fat storage and metabolism. When mice lacking this gene were fed an obesity-inducing diet, they were observed to be resistant to becoming obese!
In fact, not only did these mice stay lean, they appeared to be much healthier than the mice with a functional Plin2 gene. Compared to normal mice, their fat cells were 20% smaller, they showed an absence of fatty-liver disease, they had lower triglyceride levels, and they were more insulin-sensitive. When both normal mice and mice lacking the Plin2 gene were placed on an obesity-inducing diet, the Plin2-lacking mice showed surprising restraint when eating their food (normal mice will eat until all food is gone!), and were also more active.
What does this mean for us?
Obesity is quickly becoming a dominant health concern throughout North America (see famous chef Jamie Oliver discussing the obesity trend here), indirectly causing a long list of medical complications such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, coronary heart disease, and stroke.
The interesting thing is, humans also have a Plin2 gene. If researchers can find a way to target the Plin2 gene, these findings may result in an effective treatment for obesity. This would lead to a slimmer, healthier nation, and reduce the financial strain that obesity-related complications place on our health care systems!
However, don’t book your reservation at the neighbourhood all-you-can-eat buffet just yet. Before any human applications can be made, we must better understand what other roles the Plin2 gene may play, and how removal of this gene will influence health and behavior on a long-term scale.
– Sydney Schnell