Ever been excited to go on that road trip to your favourite destination, only to find yourself sprawled onto the seat unable to look outside because nausea hits you unexpectedly? Not to mention, this phenomenon takes place only a quarter of the way there, making the journey even longer and unbearable. From personal experience, I know exactly how that feels. But the main question is, why does this take place?
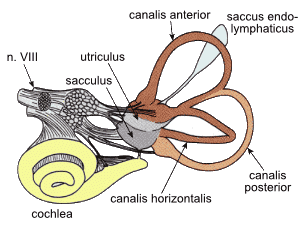
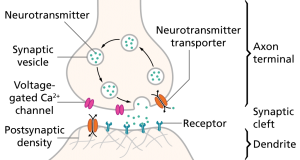
There have been many hypotheses regarding the cause of motion sickness, however, scientists are not exactly sure what the main reason is. Symptoms of motion sickness, such as nausea, vomiting, sweating, headache, dizziness, hyperventilation, drowsiness or general feeling of discomfort, are common regardless of which mode of transportation is taken. According to the British Medical Journal, a common theory of why motion sickness takes place is mismatched sensory signals between the visual and vestibular systems. The vestibular system provides balance and spatial orientation in our body by sending signals of motion to the central nervous system. In a moving vehicle, your eyes see that you are immobile because nothing in the car is moving, while your ears, which hold the vestibular system, sense that you are in fact moving. This mismatch in visual and sensory systems causes the syndrome of motion sickness.
Another reason why nausea is induced as a result of motion sickness is because of an evolutionary trait to keep the body safe from ingestion of neurotoxins. This happens when someone is sitting still, while watching a movie perhaps, and the screen is showing movement. The eyes can be deceived into believing that the body is moving while the vestibular system senses no movement. This results in an abrupt signal being sent to the central nervous system, which the body counteracts with vomit.
Although not everyone is susceptible to motion sickness, it does affect about 66% of people when they are put in more severe conditions. There are a few things you can do to decrease the severity of motion sickness. Firstly, look out the window of a moving vehicle towards the horizon of the direction you are going. To acquire optimum results, sit in the front seat since doing so visually confirms that you are moving. Secondly, chew something like gum because this can restore the balance within your body. Thirdly, close your eyes and, if you able to, nap as it is great for reducing the conflict within the visual and vestibular system. Lastly, ginger has been found to reduce motion sickness quite effectively.
For a deeper understanding of motion sickness, take a look at this video:
So next time you’re going on that long drive or vacation on a that cruise ship, use this as a guide to make sure motion sickness does not ruin your trip!
– Ravjot Ahluwalia



























![Cyanobacteria By Doc. RNDr. Josef Reischig, CSc. (Author's archive) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](http://blogs.ubc.ca/communicatingscience2015w111/files/2015/09/Cyanobacteria-300x192.jpg)

![Mars Exploration Rover By NASA/JPL/Cornell University, Maas Digital LLC [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](http://blogs.ubc.ca/communicatingscience2015w111/files/2015/09/NASA_Mars_Rover-300x240.jpg)