Hi Team BEAD,
For assignment 1:3, the objective is to identify the importance of definitions and tailoring it to the intended audience with the right level of detail.
Term and situation
The term I will be defining is photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). In this recent scenario, I am trying to convey to an engineer the theory behind measuring PAR so that we could make improvement to our lab-built spectral sensor.
Parenthetical definition
A fraction of the total incident solar radiation that could be used by plants to perform photosynthesis.
Sentence definition
Photosynthetically active radiation is a fraction of the total incident solar radiation that has a wavelength between 400 nanometer and 700 nanometer, measured in irradiance (W/m^2). Radiation in this range is characterized by it’s ability to be captured by plants to perform photosynthesis.
Expanded definition
The term photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) can be broken into two physically meaningful parts. Photosynthetically active indicates that the radiation is able to be captured by chlorophyll in the plant. This captured energy will be used by the plant to perform photosynthesis. Radiation in this context is a form of energy that only travels as an electromagnetic wave.
PAR works by providing the energy to be used by the plant to drive the photosynthetic reaction involving water (uptake through the plant’s roots) and carbon dioxide (uptake through the plant’s stomata) to create sugar for the plant.
PAR is not the same as sunlight in the visible spectrum. PAR occupies in a narrower electromagnetic range in the visible spectrum as absorbing radiation above 700nm in wavelength might damage the plant’s biomass, similar to human getting sun burned. Therefore not the entire visible spectrum 300nm to 800nm will need to be measured by the spectral sensor and we can only focus on 400nm to 700nm range.
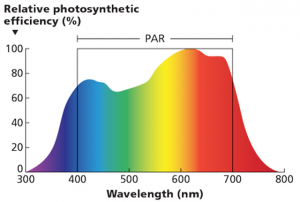
Figure 1. Image of the PAR range occupancy in the visible section of the electromagnetic spectrum. Courtesy of Jill Whitehead.
Data collected from measuring PAR can be used to calculate varies different metrics such as the theoretical productivity of the ecosystem assuming the plants are not water or nutrition limited. PAR can also show photosynthetic efficiency when compared with field based photosynthetic measurement.
References
Whitehead, J. (2019, June 6). Plant morphology and spectrum: How plants respond to light quality. Retrieved from http://pllight.com/plant-morphology-and-spectrum-how-plants-respond-to-light-quality/
Leave a Reply