In the past few decades, ecological protection has gradually become a greater concern for more and more people; however, how can we effectively protect the earth’s ecology if the vast majority of it is still alien to us, especially the ocean? Recently, we were given the chance to interview Dr.Xiong Zhang, an expert on seahorse conservation, he explained why protecting small species such as seahorses can be helpful in protecting many marine ecosystems.

Image of a seahorse
Picture retrieved from https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2016/12/15/world/science-health-world/undersea-mystery-genetic-secrets-seahorse-unveiled/

Dr.Xiong Zhang during the interview
Dr.Zhang, who is a zoology Ph.D. at the University of British Columbia, recently conducted his case study on predicting locations where seahorses are commonly found along the coastal areas in China. The main role of his study is to help protect seahorses which can improve the maintenance of many shallow sea environments. A point of interest is the reason Dr. Zhang chose seahorses, and how he believes their protection can lead to maintaining shallow sea ecosystems.
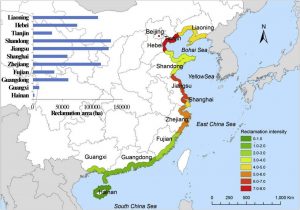
China coastal area
picture retrieved from https://medium.com/civic-analytics/signal-2-environmental-impacts-of-land-reclamation-in-china-under-climate-change-background-981edb2d7bf9
First, Dr.Zhang explained why he focuses on seahorses; there are three main reasons:
Seahorses are distributed in a variety of geological locations
Seahorses have many subspecies, and each of them requires different living conditions for habitat; for example, some prefer warm water temperatures and some prefer higher concentrations of salt. These factors make seahorses as a whole widely distributed globally, however, suitable living environments are scarce for them at the same time.
Seahorses are extremely sensitive to changes in an environment

Different types of seahorse subspecies
Picture retrieved from:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
The limitations for the seahorses are not only due to habitat requirements but also partly because of its own living habits. Seahorses need to hook on structures on the seafloor to survive; without these structures, they will drift away with the current. As a result, seahorses are confined to areas with special structures on the seafloor. The destruction on an area with such structures will lead to complete elimination of a local seahorse population.
Seahorses can be used as indicators to measure the wellness of local ecosystems
Since seahorses are “picky” in choosing their habitats, there are few places that are ideal for them, they can be used to determine whether an ecosystem is healthy. These areas often have unique characteristics, making them extremely sensitive to ecological changes. Therefore, in this particular environment, if there is a significant decrease in the number of seahorses, experts can reasonably infer that this is caused by habitat destruction.

Image of coral reef mangroves.
Picture retrieved from:
https://www.leonardodicaprio.org/protecting-coral-reefs-and-mangroves-indonesia
With all that in mind, how do we go from protecting seahorses to maintaining shallow sea environments? From previous answers, we can see that seahorses are marine animals that very dependent on their habitat; as a result, protecting their habitat is the best way to protect their population. While protecting seahorse’s habitats, we can also protect many creatures in the same environment. Using the seahorse as a starting point, we can protect organisms in a small area; when many small areas are protected, the experts will be able to maintain the ecology of the nearby shallow water on a larger scale. Therefore, protecting the seahorse is a point-to-point approach to secure the shallow sea ecosystems. Dr. Zhang’s findings effectively predict the habitat of seahorses on a large-scale from limited data, and the short video below briefly describes the process.
If the above video doesn’t work click: Video link
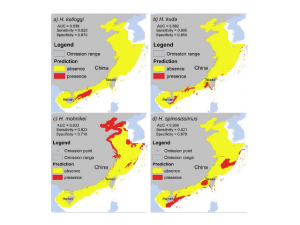
The result mapped by Dr.Zhang for 4 different subspecies of seahorses.
After drawing such a relatively precise map for the locations of seahorses, experts and authorities can make decisions of conservation more effectively. When we asked Dr. Zhang if his research had been put to practical use, he gave us a positive answer: “there is one province in the south, Guangxi province, considered my research very important and they added the seahorse habitat in the conservation planning, in its local area.”
When Dr. Zhang indicated research plans for the future, he told us: “In the future, the degree of seahorse protection will definitely increase for sure, and there are lots of local people that really care about the sustainability of the livelihood for seahorse “
In the end, Dr. Zhang told us, although we can’t say that at the current stage seahorses are well protected, but based on his research, more experts will see the importance of seahorses. Though this, more research will be focusing on seahorses in the future. Furthermore, as technology and information advance, the protection of seahorses will be more perfected. This point-to-point approach on the protection of one animal will also be more effective in protecting our shallow sea ecosystems in the future.