Ever have a headache ? fever ? you’ve probably have taken aspirin or acetyl salicylic acid in your life. Aspirin has been used by humans for more than 2500 years ever since someone had discovered that chewing willow leaves treat the discomfort. This is because of salicin which is turned into salicylic acid in the body allow for the discomfort to be treated. Chemists such as Charles Frederic Gerhardt and Felix Hoffman experimented with salicylic acid to make it last longer and make it less toxic in the body which lead to the creation of aspirin or acetyl salicylic acid. Most people have taken aspirin and enjoyed the comforts it brings in terms of fevers or headaches. But how does aspirin actually work in the body ?

Salicin the compound found in Willow leaves initially used to treat headaches , fevers and inflammation Attribution: Wiki Images (https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ab/Salicin-2D-skeletal.png )

Chemical structure of Aspirin ( Acetyl Salicylic acid ) Attribution: Sigma Aldrich http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/structure1/180/mfcd00002430.eps/_jcr_content/renditions/mfcd00002430-large.png
The body has many ways to fight an infection it could cause a fever by raising the temperature and allow the pathogens to die , it can generate immune cells to generate chemicals in order to fight pathogens and infections or they can generate other chemicals recruiting other immune cells as backup. The body has natural ways of dealing with pathogens and bacteria. Hence , aspirin should only be used when the fever is lasted longer than expected or the body temperature is fairly high. In 1971 , the discovery of the chemical prostaglandin was found to be responsible for fever , pain and inflammation. Aspirin treated these symptoms by preventing the release of prostaglandin. Prostaglandins are produced in various forms and their functions include but are not limited to increase of body temperature , stimulation of immune cells , initiation of blood clotting and much more. Prostaglandins are released from an enzyme known as Cyclooxygenase or COX. An enzyme is a chemical substance which increases the speed of a reaction. Most enzymes require a missing piece , known as a substrate , this substrate binds to the enzyme and activates it in order to speed up the reaction taking place. Cyclooxygenase’s substrate is known as Archidonic acid , when this substrate binds to the enzyme it releases prostaglandins so they can act on the body and cause inflammation , pain and a rise in temperature.

The production of prostaglandin from the enzyme COX Attribution: Wiki images https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/07/Prostaglandin_E1.svg/1486px-Prostaglandin_E1.svg.png
When you take aspirin or acetyl salicylic acid , it binds to the enzyme COX (cyclooxyengease) and prevents its substrate (Archidionic acid) to bind. The acetyl salicylic acid binds irreversibly , meaning that it does not unbind easily and requires energy for it to unbind from the enzyme. The loss in production of prostaglandins results in less inflammation , pain and fever.
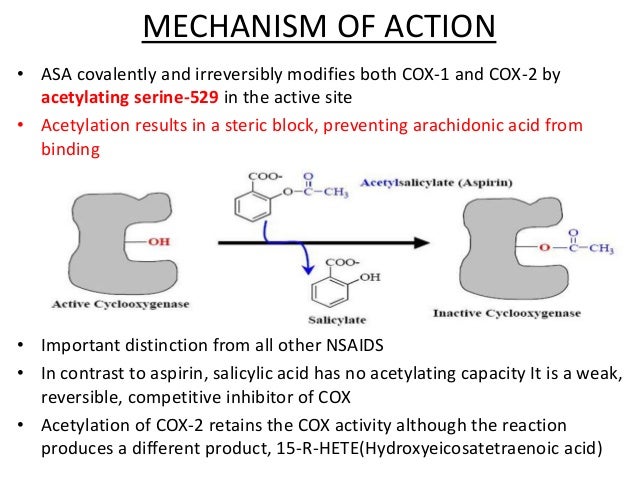
Summary of Aspirin blocking the enzyme COX irreversibly Attribution: Slide share https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cox-170117123110/95/nsaids-cox-enzymes-physiologyand-pharmacological-modulation-20-638.jpg?cb=1486012928
However , prostaglandins are also responsible for blood clotting and if they are blocked from being produced , blood clotting will not occur as effectively. Aspirin should be taken with care and only when required. Other medication such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) are a better substitute in the case of the fever or body temperature not being as high. Some people might think an alternative to medication are “natural” remedies that directly arise from plant based foods. They tend to forget that medication is synthesized from plants. I believe that medication is the way to go for the best treatment of most type of illness. So next time you take an aspirin you can be thankful for that willow plant someone ate a few thousand years ago !
– Garvit Bhatt
