Tiny chemical molecules called amino acids interlock with other amino acids via a covalent linkage called a peptide bond, forming protein macromolecules. Proteins are necessary for our body to be able to function properly and to carry out the daily essential life processes. Proteins are required for building tissues and muscles, digesting and the uptake of nutrients, and helping to maintain homeostasis throughout the body. The protein that is readily available for us humans to intake comes from the foods we eat. More specifically, foods that are high in protein are: beans, almonds, broccoli, Greek yogurt, and most importantly meat!
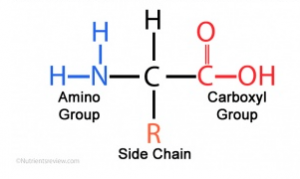
A generic depiction of the chemical structure of an amino acid. Source: https://teaching.ncl.ac.uk/bms/wiki/index.php/Amino_acids
Researchers have proven that there is a distinct correlation between the types of meat people consume, and the types of cancers you may be diagnosed with. Studies show a variety of meat such as red pork, beef and goat are a possible cause of colorectal cancer. Colorectal cancer develops in the colon when cells start to proliferate rapidly without any control. From here, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body. Colon cancer is the third most common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
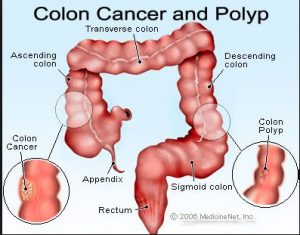
Diagram of the colon, and the targets for colon cancer to develop. Source: https://www.medicinenet.com/colon_cancer/article.htm#what_is_cancer
Now, why is this relevant to us and our daily lives? A majority of the world’s population consumes some sort of meat throughout their lives, and even eat it on a regular basis. Television and social media advertise the amazing tasting bacon, steak and burgers you can get from restaurants or your local grocery stores. People who wish to bolster their physique by lifting weights also require a high protein intake in order to build-up the muscle.

Source: https://www.cancercouncil.com.au/21639/cancer-information/cancer-risk-and-prevention/healthy-weight-diet-and-exercise/meat-and-cancer/
Undercooking meat products raises a huge issue based on developing cancer. The “rarity” and redness found in your steak and/or beef cause an alteration in the chemical composition of another essential macromolecule in DNA, which stores hereditary information in the form of gene segments or chromosomes. The reason why “medium-rare” steaks, red beef and pork are accountable for changing the outlook of DNA is because of the vast amount of hemoglobin contained within it. The hemoglobin can turn into N-nitroso compounds, which are suspected cancer-causing agents. Hemoglobin is a type of protein in blood which is responsible for transporting oxygen. This is due to its iron subunits being bound to a heme group and their ability to bind to oxygen atoms, thus becoming a red-looking myoglobin protein.
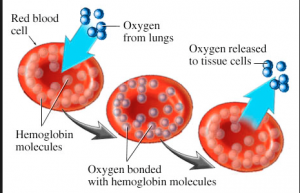
Shows hemoglobin transporting oxygen throughout our blood. Source: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/hemoglobin
Up until this point, I’ve been talking about how undercooking meat and the blood contained within meat may be detrimental towards your health. However, what’s the difference between this and processed meats?
Processed meats are meats that have been smoked and salted by the addition of preservatives. Some common examples may be packaged goods you find at your local grocery store; ham, bacon, hot dogs etc…
Further studies show that the preservatives in processed meats have a higher concentration of nitrosamines, which are carcinogens, than any other meat products.
In today’s society that we live in, with all the advancements in scientific research and technology, we are discovering many different factors that can ultimately lead to the causes of several cancers. The take-home message would be, even though extensive research has shown that certain meat products are behind the diagnosis of cancer, eating in moderation has never lead to harm. Cancer is this great complex phenomenon that requires the contribution of biological, physical and environmental factors to cause it. While changing your lifestyle to avoid eating meats has its many benefits, from a personal standpoint, I can’t go a day without having some type of poultry. In spite of this, from researching about this topic I have become more contentious of what I put into my mouth.
Author: Simranjit Singh
